jelaskan apa itu tubulus seminiferus...
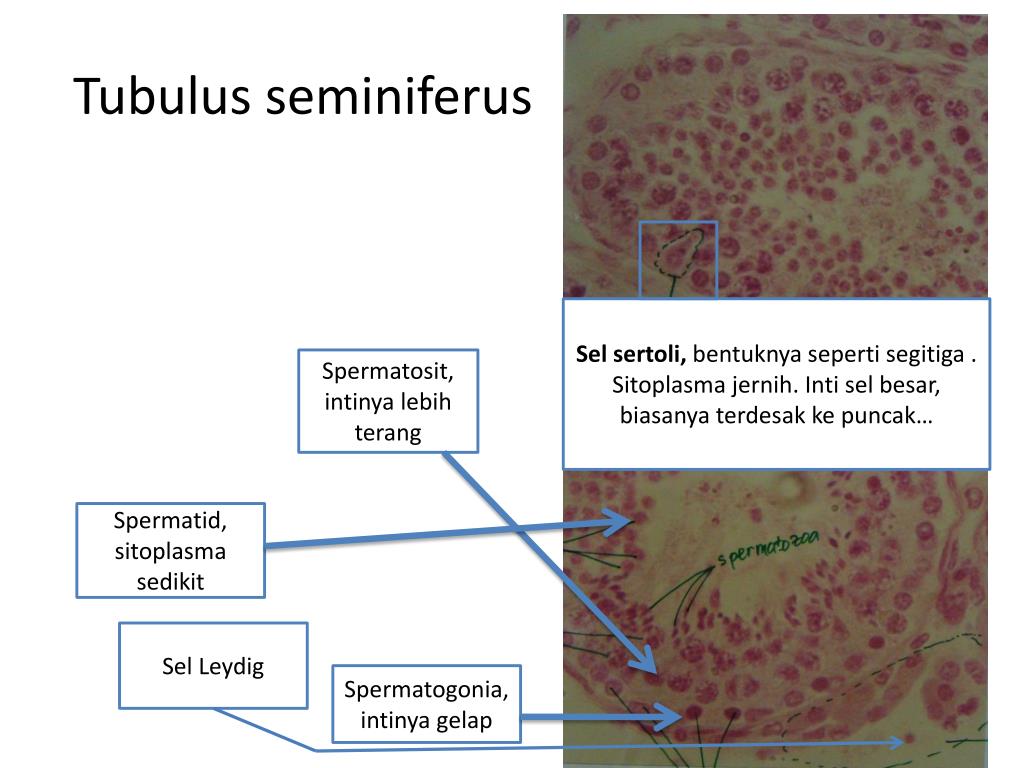
Seminiferous Tubules. The seminiferous tubules provide a unique environment for the production of germ cells. The structures involved in this process include germinal elements and supporting cells. The supporting cells include the peritubular cells of the basement membrane and the Sertoli cells. The germinal elements comprise a population of.

PPT MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2000162
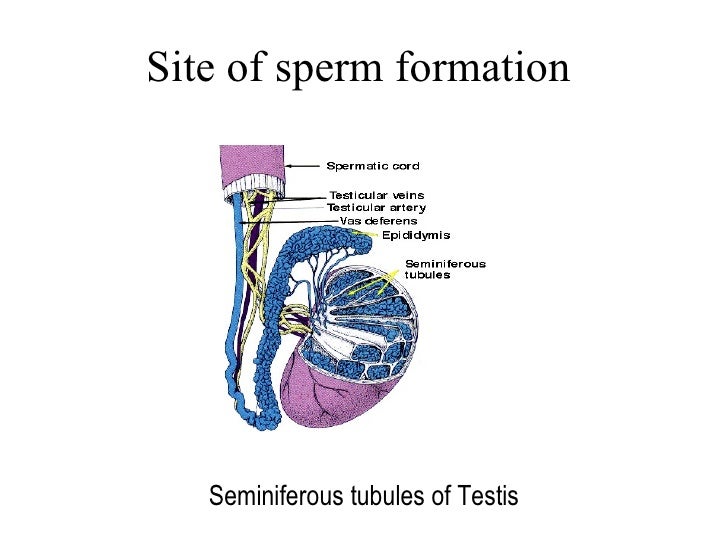
The testes. Seminiferous tubules comprise the bulk (80%) of the testis mass and are responsible for developing germ cells. Support cells include Sertoli cells, fibrocyte, and myoid cells. The interstitium between the seminiferous tubules contains blood vessels, lymphatics, Leydig cells, mast cells, nerves.

Human Testicles Anatomy, Inside Structure, Function and Location
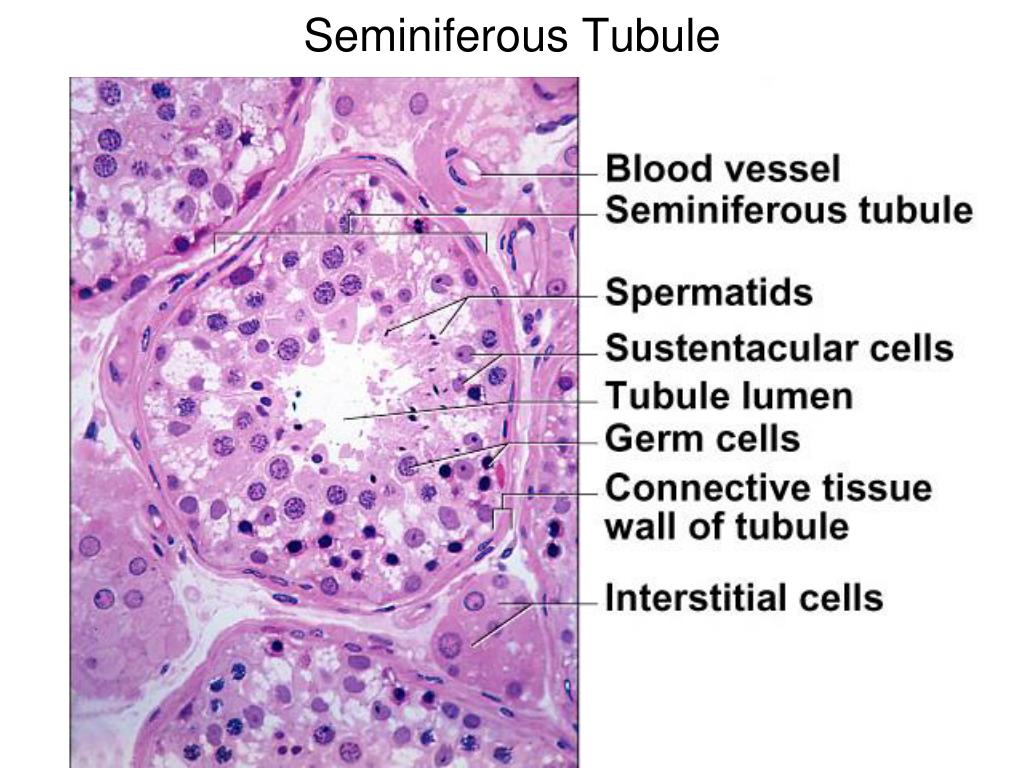
Reproductive - Histology of seminiferous tubules View Related Images. Description: This image is a histological section of the seminiferous tubules.
Male Seminiferous Tubules
Within the seminiferous tubules, somatic Sertoli cells extend from the basement membrane adjacent to PTM cells to the lumen and surround the developing germ cells (Figure 16.1(C)).Germ cells are present throughout the seminiferous tubule epithelium, with the most immature and undifferentiated cells, including spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), present on the basement membrane and the most.

Seminiferous tubules Stock Image C012/1237 Science Photo Library
We developed a technique to analyze the high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) structure of seminiferous tubules. It consists of segmentation of tubules in serial paraffin sections of the testis by marking the basement membrane with periodic acid-Schiff or a fluorescent anti-laminin antibody followed by 3D reconstruction of tubules with high-performance software. Using this method, we.
jelaskan apa itu tubulus seminiferus...
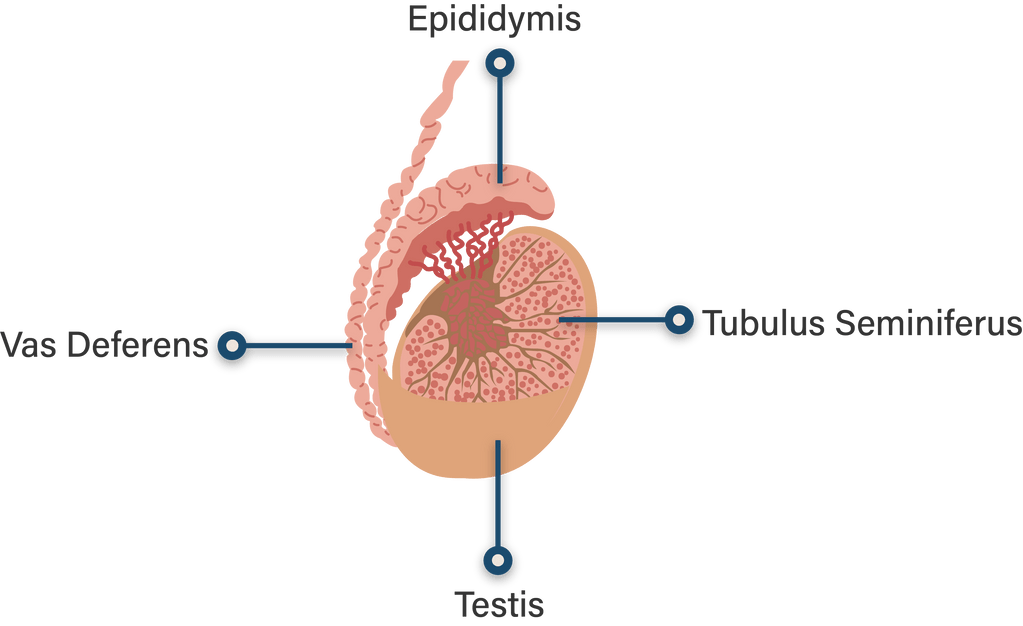
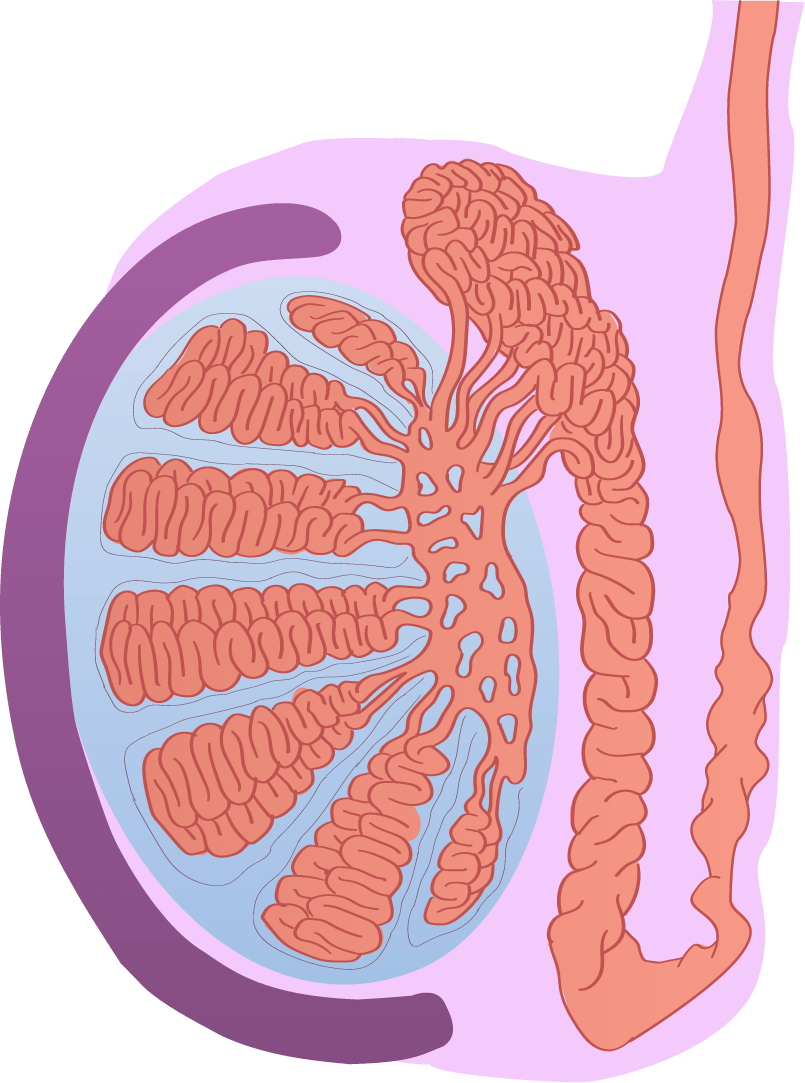
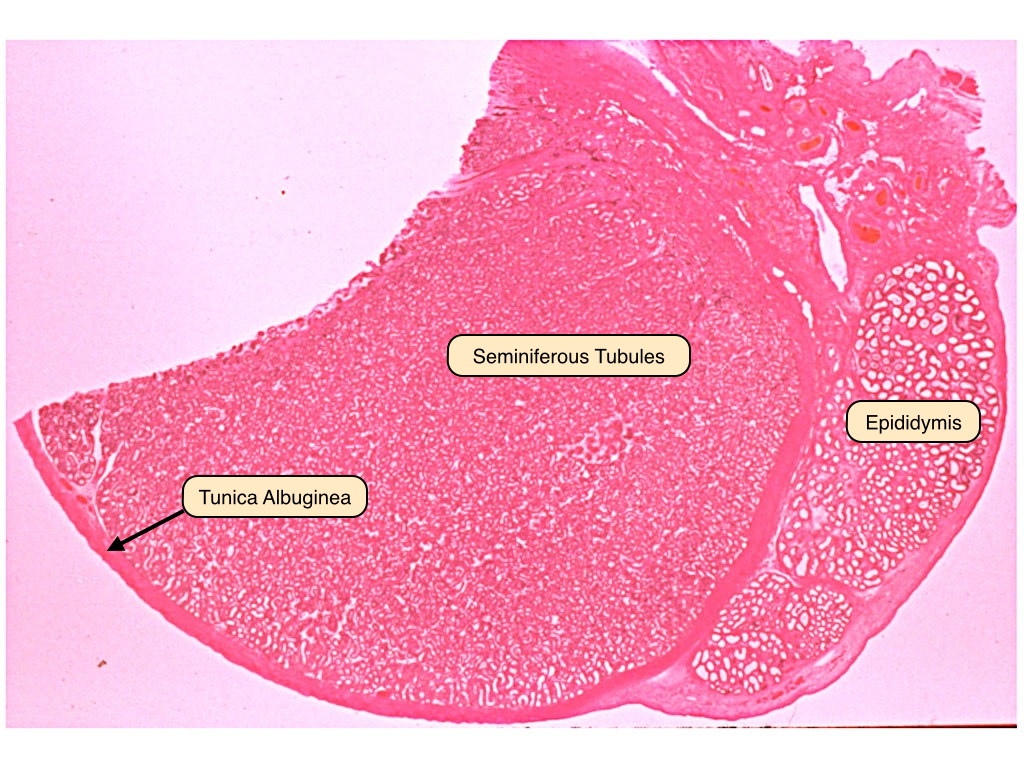
Definition. Each lobule of testis is contained in one of the intervals between the fibrous septa which extend between the mediastinum testis and the tunica albuginea, and consists of from one to three, or more, minute convoluted tubes, the convoluted seminiferous tubules.

Male Reproductive System Lab
A simple structure is observed uniformly throughout the entire length of the ~ 2 m (!) long seminiferous tubules, which is tightly packed within a single mouse testis (Fig. 3) (Hilton & Turner, 1993; Russell et al., 1990; Yoshida, 2018a).Sertoli cells and two layers of peritubular myoid and lymphatic endothelial cells along with a basement membrane compose the basic structural framework of.
PPT Organ Reproduksi Pria PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4739934
Other articles where seminiferous tubule is discussed: animal reproductive system: Testes:.testes are composed largely of seminiferous tubules—coiled tubes, the walls of which contain cells that produce sperm—and are surrounded by a capsule, the tunica albuginea. Seminiferous tubules may constitute up to 90 percent of the testis. The tubule walls consist of a multilayered germinal.
PPT Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID883757
Seminiferous tubules have a highly simple and uniform structure over their total lengths of up to 2 m coiled within the mouse testis ( Hilton & Turner, 1993; Russell et al., 1990; Yoshida, 2018a ). SSCs are scattered over the basal compartment with strikingly constant average densities ( Kitadate et al., 2019 ), making it simple to obtain large.
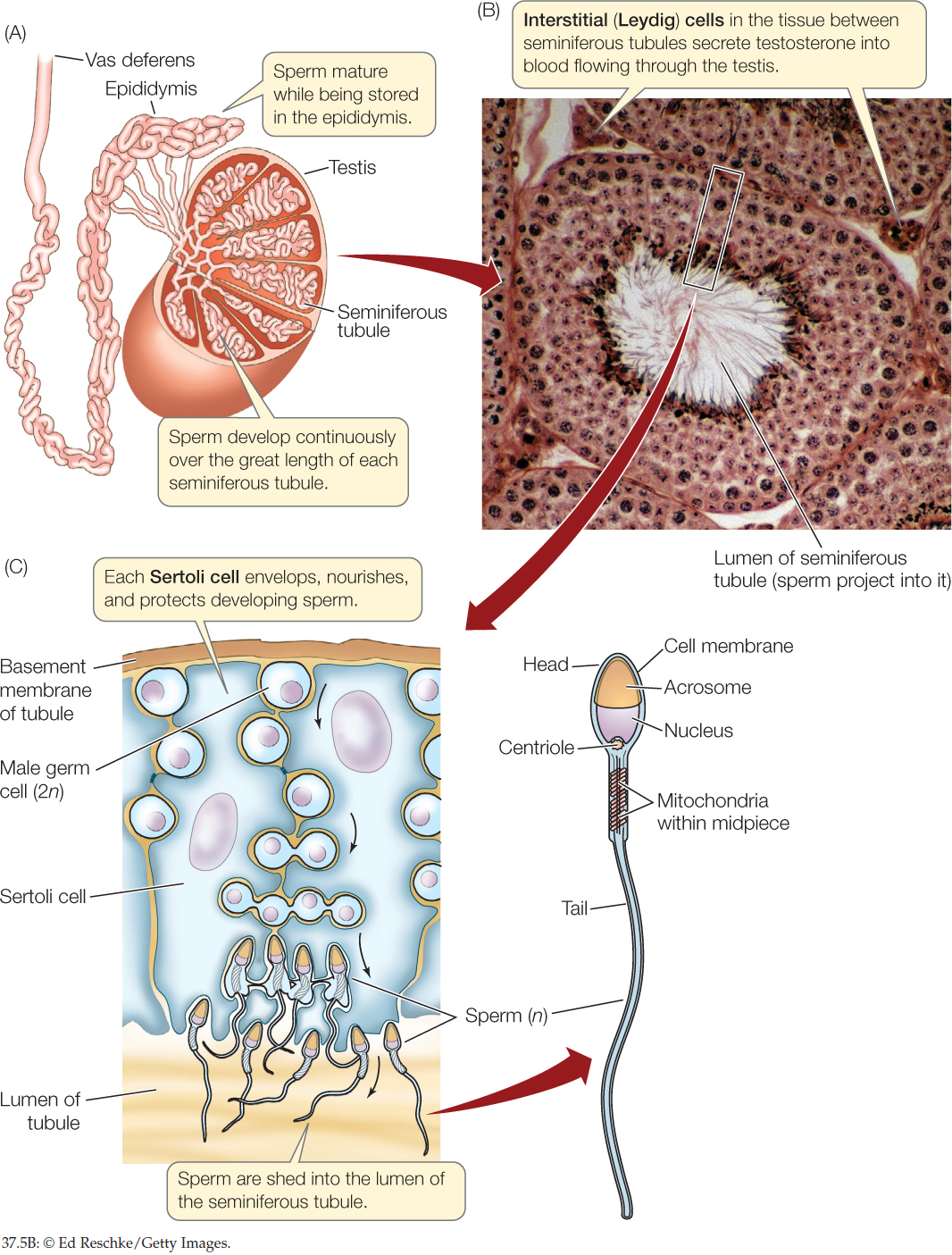
Figure 37.5
The tubuli seminiferi recti (also known as the tubuli recti, tubulus rectus, or straight seminiferous tubules) are structures in the testicle connecting the convoluted region of the seminiferous tubules to the rete testis, although the tubuli recti have a different appearance distinguishing them from these two structures.

Gambaran Histologi Tubulus Seminiferus Dari Sediaan Testis Mencit
Abstract. The testis is made up of the seminiferous tubules, where the spermatozoa develop, and interstitial cells (Leydig cells), where testosterone is produced. The seminiferous tubules are long U-shaped tubules which form their U-turn at the periphery of the testis as both distal ends drain toward the central superior and posterior regions.

Gambar 3. Atrofi tubulus seminiferus terjadi pada tubulus seminiferus... Download Scientific
The seminiferous tubules are the site of the germination, maturation, and transportation of the sperm cells within the male testes. Seminiferous tubules are made up of columnar Sertoli cells surrounded by spermatogenic cells on the epithelial interior and stem cells exteriorly. Spermatogenesis through the process of meiosis takes place within.

PPT Chapter 5 Male Sexual Anatomy & Physiology PowerPoint Presentation ID1111208
One of the major concerns of the world health community is the infertility. The definition of infertility according to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) is the inability of a healthy couple to achieve a conception after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse. Fertility complications affect seven percent of the male. The causes.

Struktur, Bagian, dan Fungsi Alat Reproduksi LakiLaki Materi Sistem Reproduksi Biologi
Seminiferous tubules develop from sex cords, which are embryonic structures with simple C-shaped arches. Histologically, the epithelium of adult mouse seminiferous tubules has been divided into 12 stages based on the associations of spermatogenic cells in four cycles of spermatogenesis. However, the gross characteristics of the seminiferous.
Seminiferous Tubules
Seminiferous tubule. Seminiferous tubule in cross-section (large tubular structure - center of image) with sperm (black, tiny, ovoid bodies furthest from the outer edge of the tubular structure). H&E stain. Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male.

Post Medizzystructure Of Testis learnbrainly.live
During the third [ (, or condensing spermatid)] stage, the [spermatids] become fully developed. The filament for the formation of the midpiece [ (of the flagellum, or tail)] connects to the head. The cellular protoplasm gradually disappears, generating the well-known appendage joined to the midpiece.