
Difference between Transport Layer and Network Layer Scaler Topics
In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. [1] : §1.1.3 It provides services such as connection-oriented.
TLS 1.2 Transport Layer Security Protocol Accuenergy
The transport layer is a 4 th layer from the top. The main role of the transport layer is to provide the communication services directly to the application processes running on different hosts. The transport layer provides a logical communication between application processes running on different hosts. Although the application processes on.
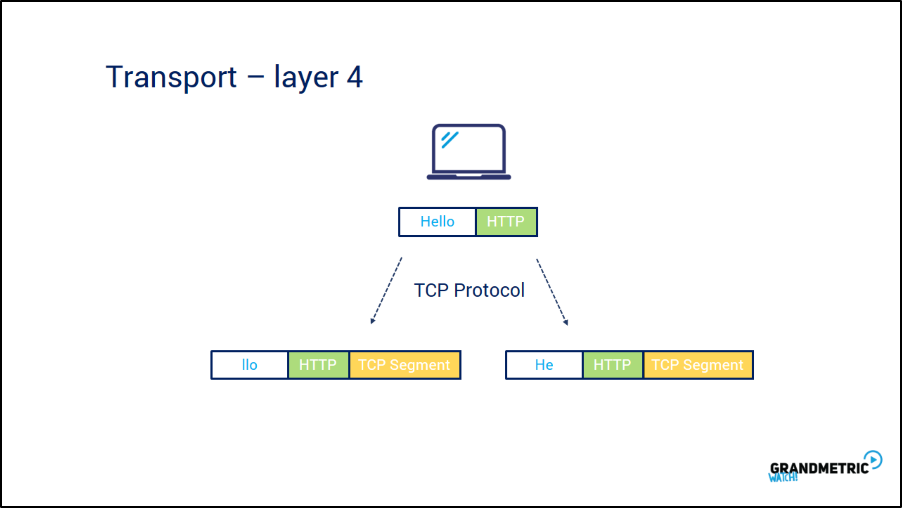
transportlayer Grandmetric
The transport layer is the fourth layer in the OSI and TCP/IP layers models. It manages the transport of data between two hosts over a network. Since the data can be transmitted into small chunks called data segments, it breaks the data stream into segments and attaches the necessary information to reassemble them back into the data stream on.
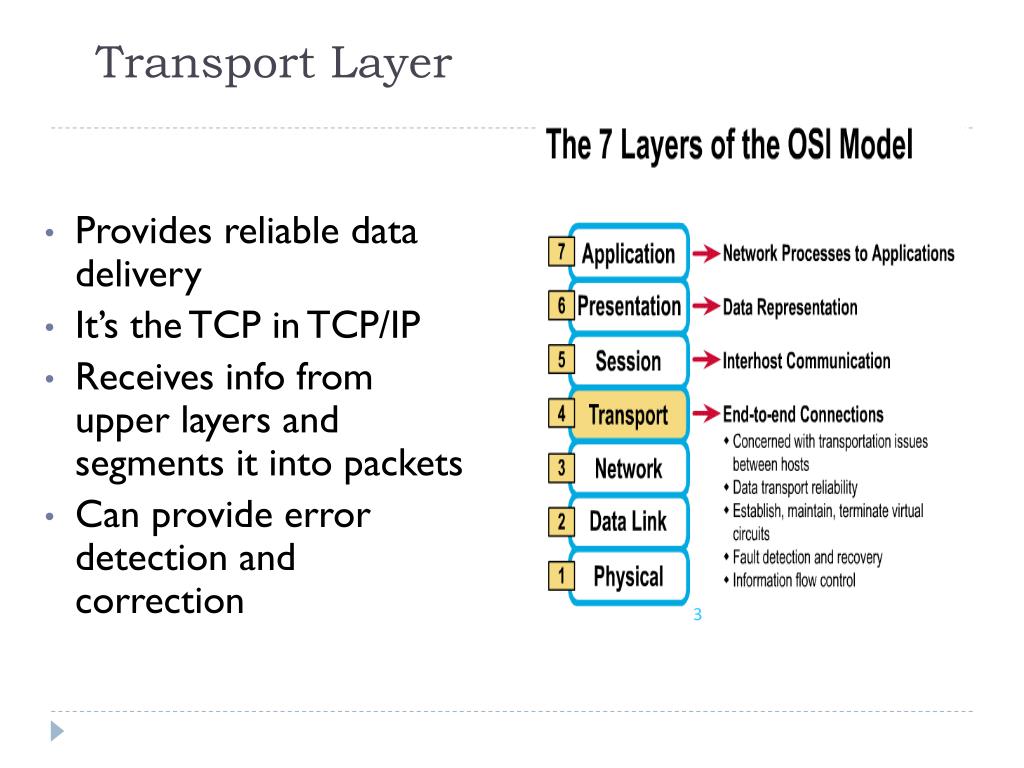
PPT Transport Layer PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5644720
The transport layer is the fourth layer in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model and is responsible for end-to-end communication on the network. It provides logical communication between the layered architecture of the protocol and application processes running on different hosts in other network components.

Top 6 major functions of transport layer in network
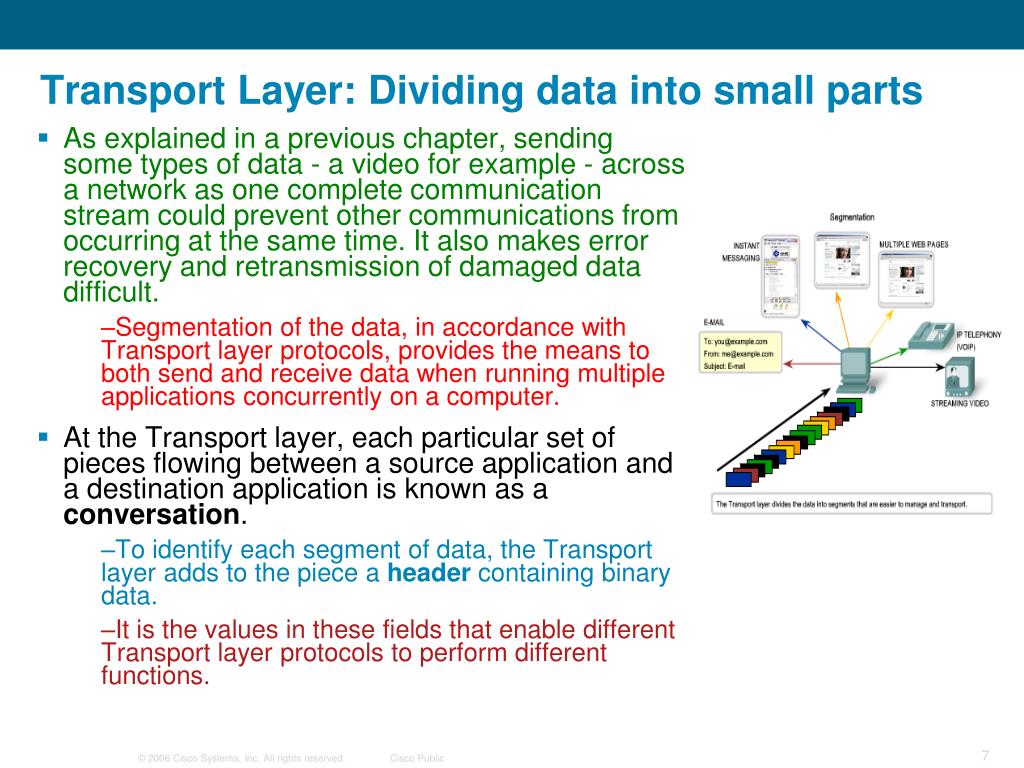
The tasks of the transport layer (also end-to-end control, transport control) include the segmentation of the data stream and in relieving congestion. A data segment is a Service Data Unit, which is used for encapsulation on the fourth layer (transport layer). It consists of protocol elements that contain Layer 4 information control.
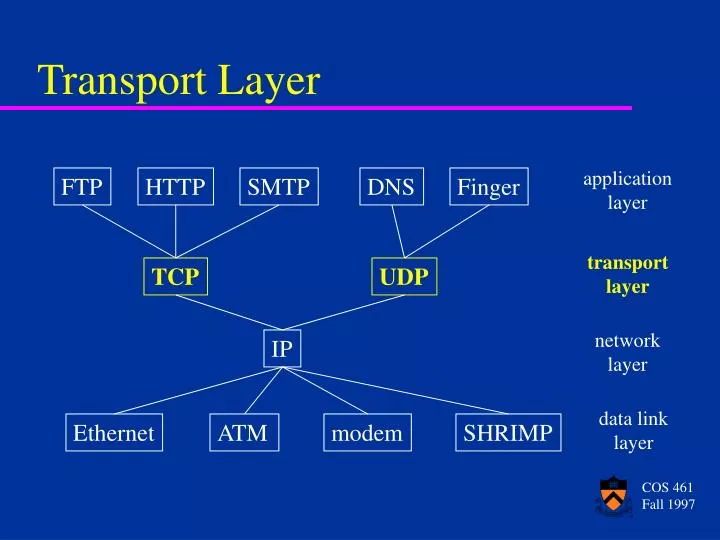
PPT Transport Layer PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4982663
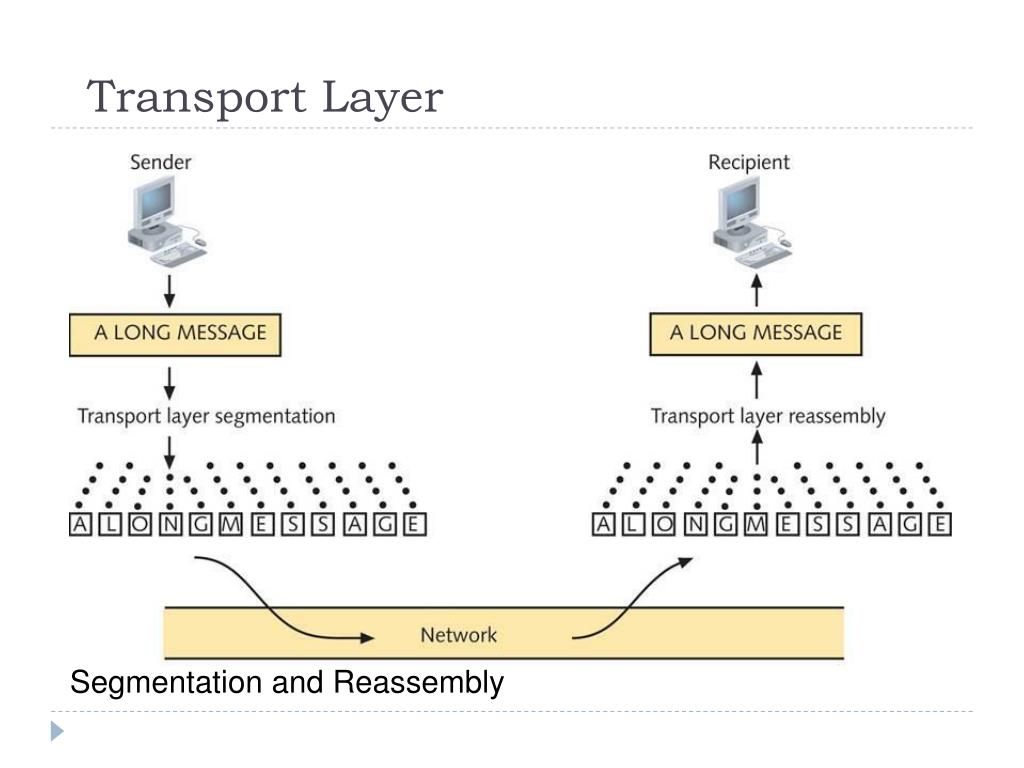
The transport layer breaks data into chunks (called segments) to send them, then the receiving device reassembles the segments before the network layer breaks them into smaller packets to send to other networks. The data link layer facilitates data transfer between devices on the same network, and, finally, the physical layer transfers data in.
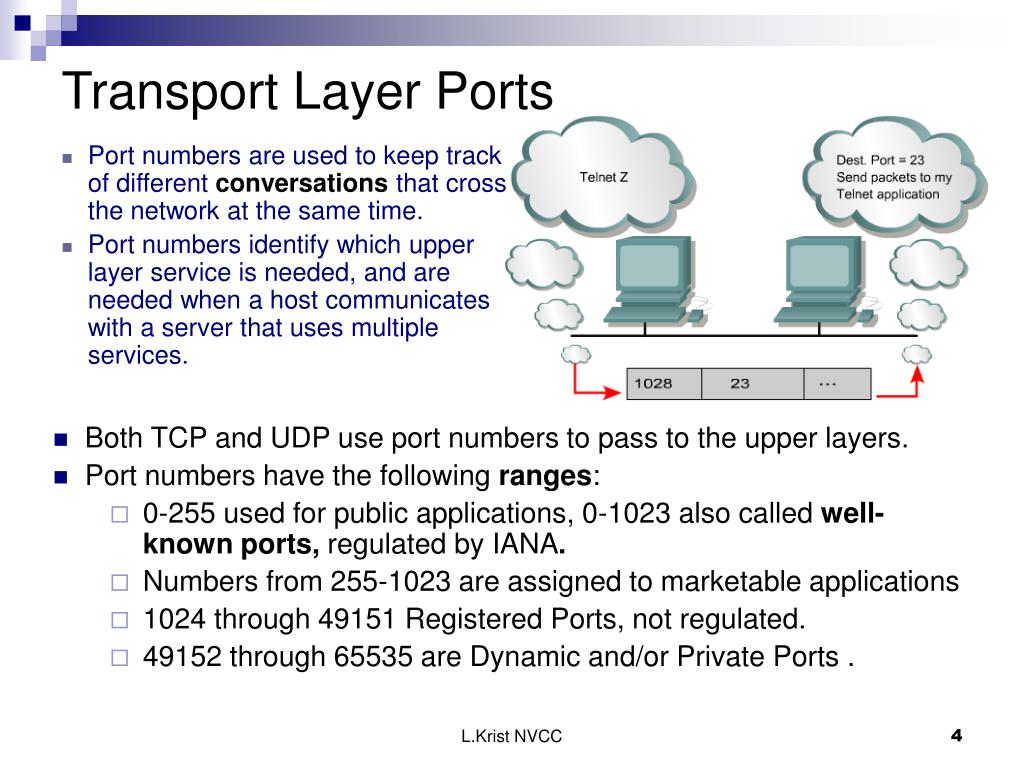
PPT Transport Layer Protocols TCP and UDP PowerPoint Presentation
The transport layer takes the services from its upward layer which is the application layer and provides it to the network layer. Segment is the unit of data encapsulation at the transport layer. In this article, we are going to discuss all the important aspects of Transport Layer Protocol which include: Functions of Transport Layer protocol.
PPT OSI Transport Layer PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Transport Services Access Point (TSAP): A Transport Services Access Point (TSAP) is an end-point for communication between the Transport layer (layer 4) and the Session layer in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) reference model. Each TSAP is an address that uniquely identifies a specific instantiation of a service. TSAPs are created by.
How the Transport Layer Works (And How Transport Protocols Work!)
The transport layer entity interacts with both a user in the application layer and the network layer, to make the network layer's data usable by applications. From the application's viewpoint, the main limitations of the network layer service come from its unreliable service: The network layer may corrupt data. The network layer may lose data.

Transport Layer Basics
The transport layer¶ As the transport layer is built on top of the network layer, it is important to know the key features of the network layer service. There are two types of network layer services : connectionless and connection-oriented. The connectionless network layer service is the most widespread. Its main characteristics are :
PPT Transport Layer PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5644720
The Transport layer is the layer-4 of the OSI reference model. The transport layer is mainly responsible for the process-to-process delivery of the entire message. A process is basically an application program that is running on the host. The basic function of the Transport layer is to accept data from the layer above, split it up into smaller.
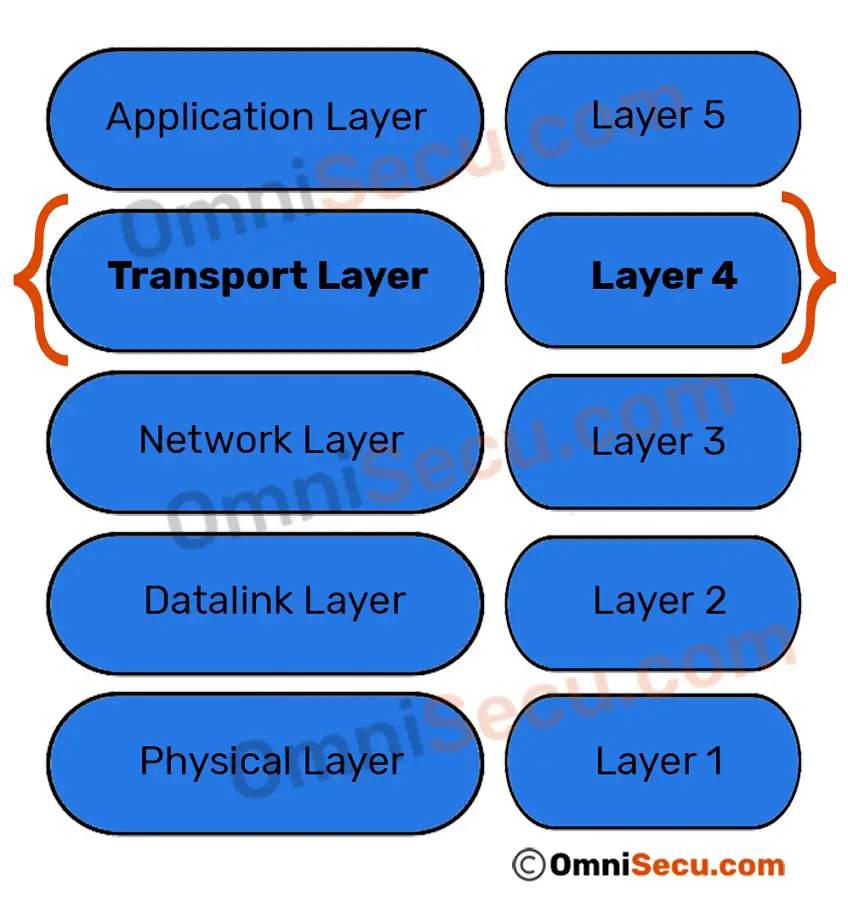
Transport Layer (Layer 4)
The transport layer is responsible for facilitating host-to-host communication between applications on two different hosts. Depending on the protocol used, it may also offer services such as reliability, flow control, sustained connections, and more. When writing a networked application, your application typically interfaces with the transport.

Transport Layer Introduction YouTube
The transport layer ensures that your request gets delivered to the process running the web server on the remote host, while returning the web page to your web browser process. In contrast to a monolithic entity like an OS, the network is a layered architecture of distributed components that cooperate to exchange data. For a variety of reasons.
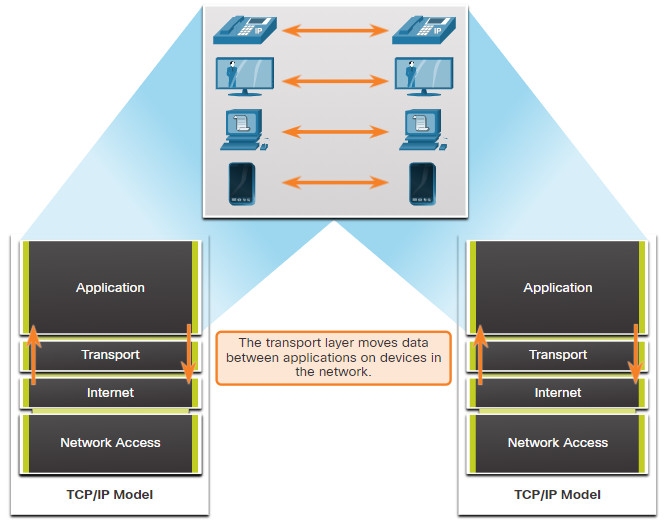
CCNA 1 v7.0 Curriculum Module 14 Transport Layer
Transport Layer: The transport layer is the layer in the open system interconnection (OSI) model responsible for end-to-end communication over a network. It provides logical communication between application processes running on different hosts within a layered architecture of protocols and other network components. The transport layer is also.
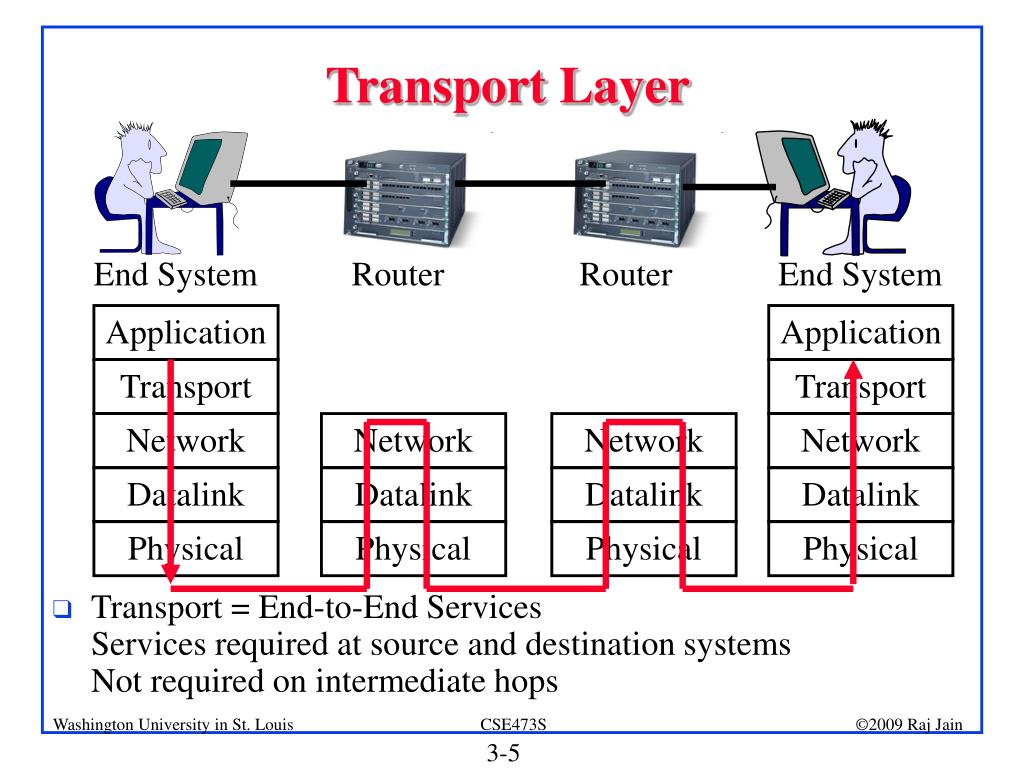
PPT Transport Layer PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5864860
The transport layer, or layer 4 of the OSI model, controls network traffic between hosts and end systems to guarantee full data flows. Data volume, destination, and rate are all controlled by transport-layer protocols including TCP, UDP, DCCP, and SCTP. The transport layer is positioned between the network and session layers in the OSI paradigm.

Space Development Agency Awards Two Transport Layer Contracts For
In this article, we will concentrate on Layer 4, which is the Transport Layer. The upper layers, the Application Layer, Presentation Layer, and Session Layer, are responsible for preparing and sending the raw data. In contrast, the lower layers, the Network Layer, Data Link Layer, and Physical Layer, are responsible for encapsulating the raw.