
Porous Fabric
Translation for 'porous' in the free English-Indonesian dictionary and many other Indonesian translations.
Q&A 3 What are porous media? News May 24, 2019 Sonderforschungsbereich 1313 University
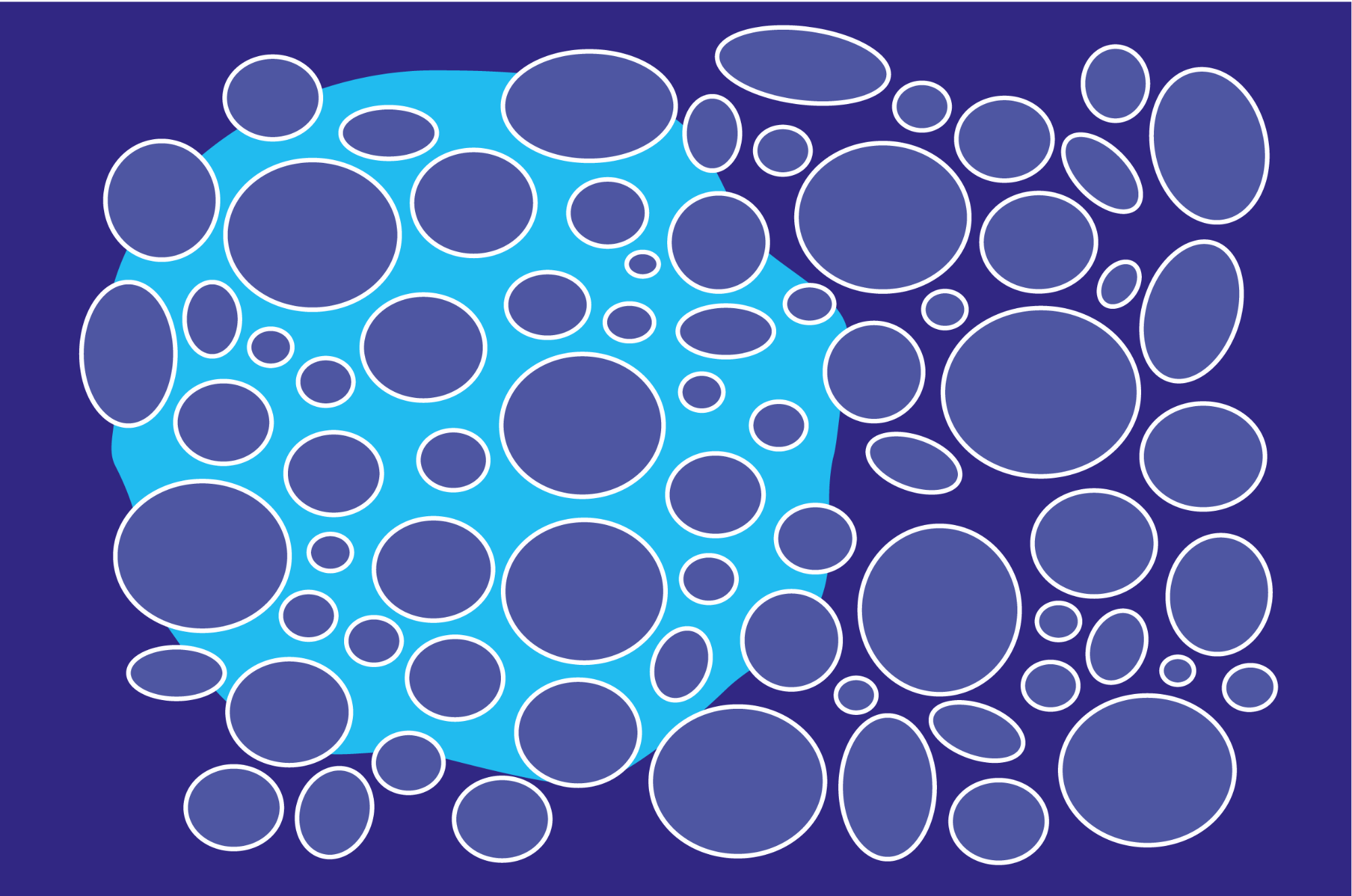
2.1 Porosity. The porosity is a vast area of concept, can be defined by many terms such as different pore morphologies, pores materials incorporated, pore size, and furthermore, considered on application (Betke and Lieb 2018).From Porosity, we can perceive nature of a material and produce advanced structures (Jiang et al. 2009).The major structural factors of a porous material or polymers are.

Is Wood Porous or Non Porous? Common Questions About Wood are Answered
Porous materials can be classified into microporous, mesoporous, and macroporous materials based on pore size, and their synthesis methods include self-templating, soft-templating, hard-templating, and so on. The key scientific issues in current porous materials research can be divided into two categories: (1) engineering of pore structures; (2.
Porous
where \(k^{{{\text{eff}}}}\) is the bulk (effective) electrical conductivity of the porous material completely saturated by electrolyte, \(k^{0}\) is the conductivity of the electrolyte, and \(\psi\) is the ratio of the apparent cross-sectional area of the conducting electrolyte to the total cross-sectional area of the specimen. This ratio, however, varies from one cross section to another.

MEDIA TANAM POROUS ARTINYA MENGENAL LEBIH DEKAT MEDIA TANAM POROUS YouTube
portend. portent. porter. portfolio. Terjemahan lebih lanjut di kamus bahasa Indonesia-bahasa Inggris oleh bab.la. Terjemahan untuk 'porous' dalam kamus bahasa Indonesia gratis dan banyak terjemahan bahasa Indonesia lainnya.
Porous Materials
Sebastian Henke. Nature Communications (2023) Porous materials contain regions of empty space into which guest molecules can be selectively adsorbed and sometimes chemically transformed. This has.

Porous vs. NonPorous Surfaces What's the Difference (January 2024)
Keywords: stochastic image reconstruction, porous media, arti cial neural networks I. INTRODUCTION A. Image Reconstruction The reconstruction and the evaluation of the material properties of porous media plays a key role across many engineering disciplines. Many physical processes such as the movement of multiple phases of uids through sedi-

12 Types of Porous Rocks (With Examples of Porous Rocks) Yes Dirt
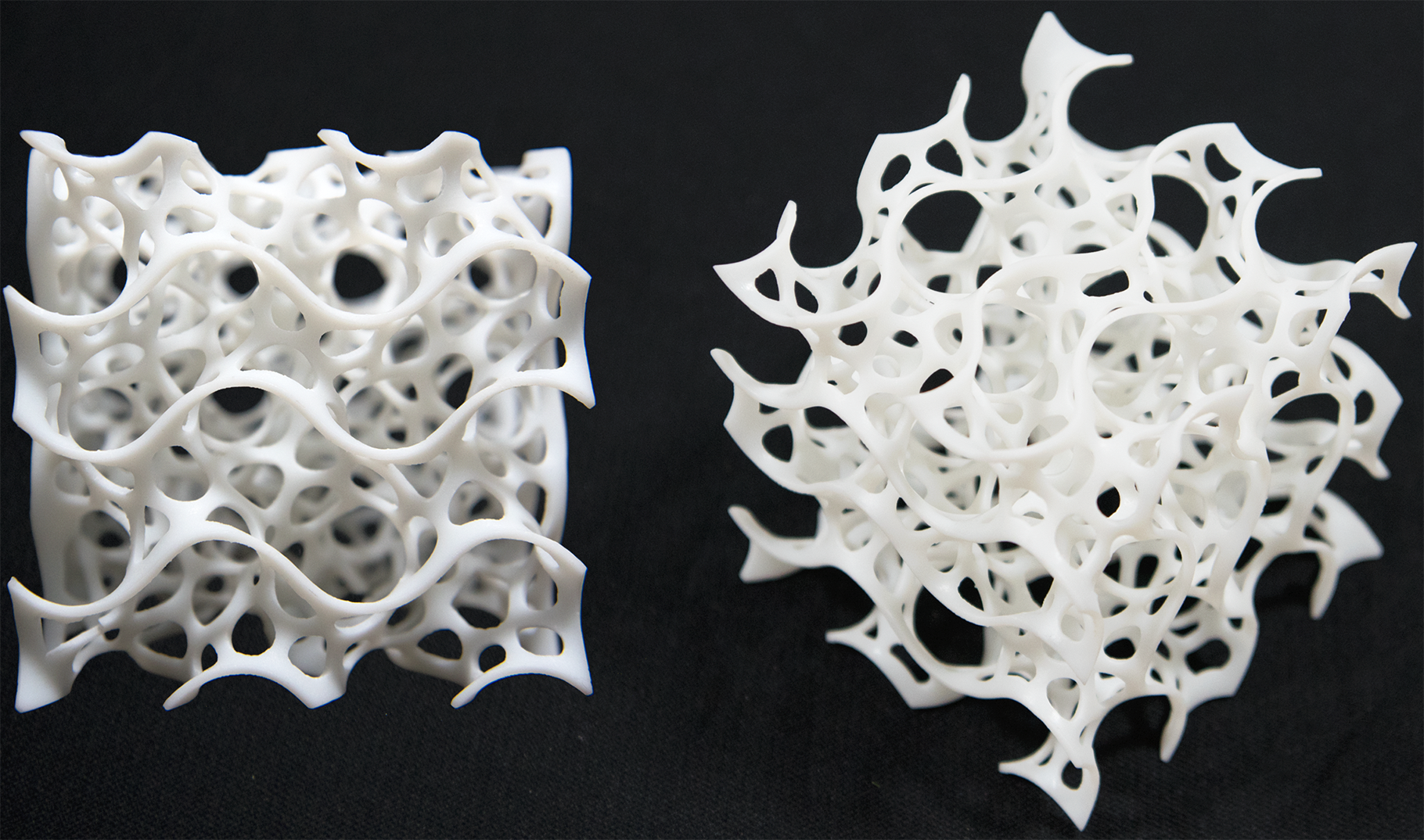
The development of porous materials is accompanied with the demands of society. A large number of porous materials have been designed and synthesized Fig. 1.1 Illustration of porosity existing in nature. The visual example is honeycomb Fig. 1.2 Porous materials could be classified according to their pore size and their components
Porous
Porous Janus materials, featured by asymmetric properties on two opposing surfaces, can be organic, inorganic, or hybrid/composite [37].In comparison with microscopic Janus particles [38] and nanosheets [39], the porous Janus materials that we review here are macroscopic and promise wider applications.To date, a variety of asymmetric properties have been exploited, which can be independent bi.

Beton Porous PT. VARIA USAHA BETON
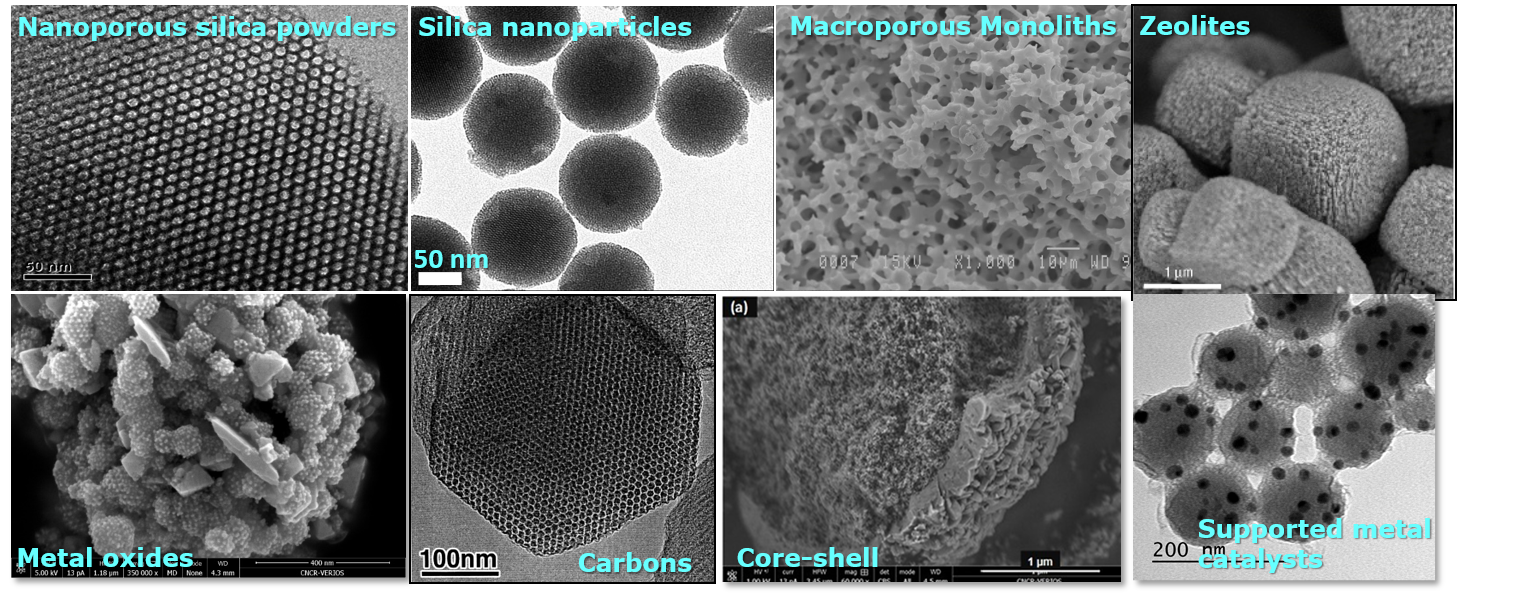
Porous crystalline frameworks including zeolites, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), covalent organic frameworks (COFs) and hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks (HOFs) have attracted great research interest in recent years. In addition to their assembly in the solid-state being fundamentally interesting and aest Materials Horizons 10th anniversary regional spotlight collection: The Americas.

Porous structures (SEM) of A D10, B D20, C D30, D E10, E E20, and... Download Scientific
Porous Asphalt is a pervious pavement designed to allow stormwater infiltration through the surface into the soil below. The water is naturally absorbed and filtered, and the pollutants are removed. In contrast, regular asphalt pavement is an impervious surface that sheds and repels rainfall and surface pollutants.

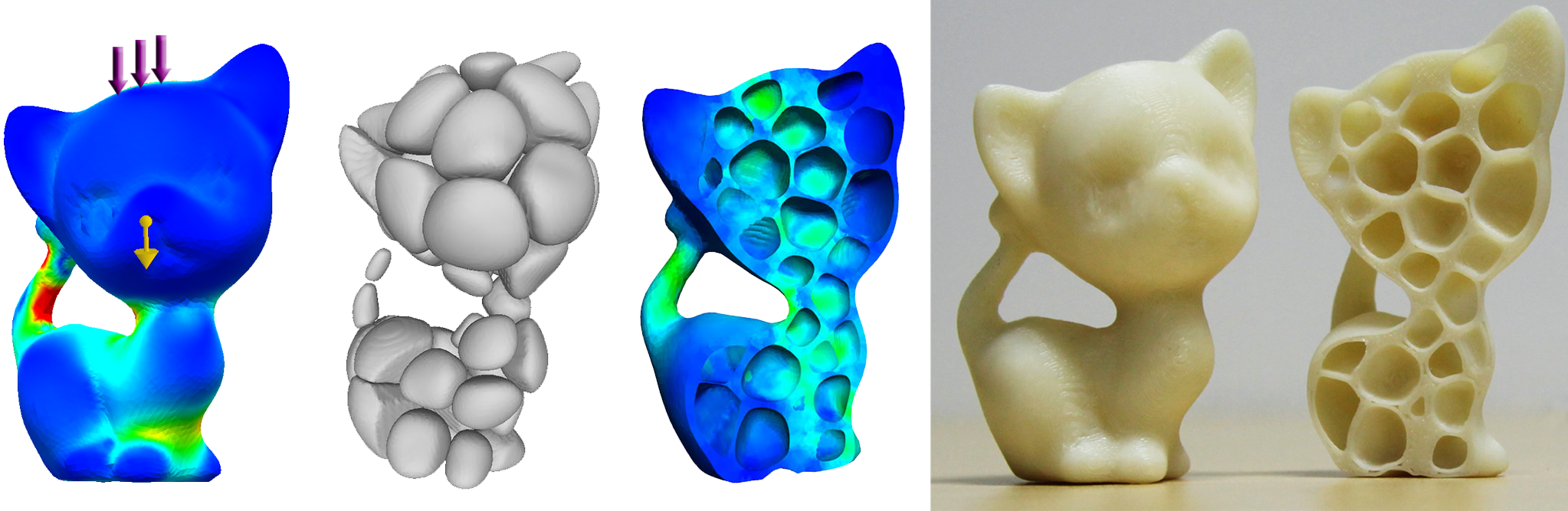
Trabecular and porous structure for a better osteonintegration
2.1. Definitions and measurements of porous materials. Porosity is defined as the void of material, and is further characterized by the interconnections, or throats, between these pores, and walls or struts of the medium which forms the 3D structure (Figure 1). []Features of pores, throats, or struts are characterized by their size, shape, organization, density, and homogeneity.

Crystal structures of typical porous materials and the advantageous... Download Scientific Diagram
Porositas bebatuan. Bebatuan terkonsolidasi seperti batu pasir, shale, granit, atau batu kapur umumnya memiliki dua sifat porositas jika dibandingkan dengan sedimen aluvial. Sifat porositas tersebut yaitu porositas terhubung dan porositas tidak terhubung. Porositas terhubung dapat diukur dengan menggunakan gas atau cairan yang mengalir ke dalam.

Differences Between Porous Wood and Non Porous Wood
The other plank wood definitely appears to be a ring porous wood, but I am easily fooled sometime by the semi-ring porous woods, i.e. ask, to me, seems to have distribution of pores well into the early wood growth; or, true hickory woods, for example, also seem more alike semi-ring porous although defined as ring-porous. Anyway… thanks again.

SEM images of the porous and nonporous silica particles. Mesoporous... Download Scientific
Mesoporous material. Electron microscopy images of nitrogen-containing ordered mesoporous carbon (N-OMC) taken (a) along and (b) perpendicular to the channel direction. [1] A mesoporous material (or super nanoporous [2]) is a nanoporous material containing pores with diameters between 2 and 50 nm, according to IUPAC nomenclature. [3]

Porous volcanic rock Stock Image C004/5193 Science Photo Library
The resulting catalysts exhibit a complex hierarchical pore arrangement arising from each component's pores as well as their inter- and intra-connectivity. The pores' architectures were.