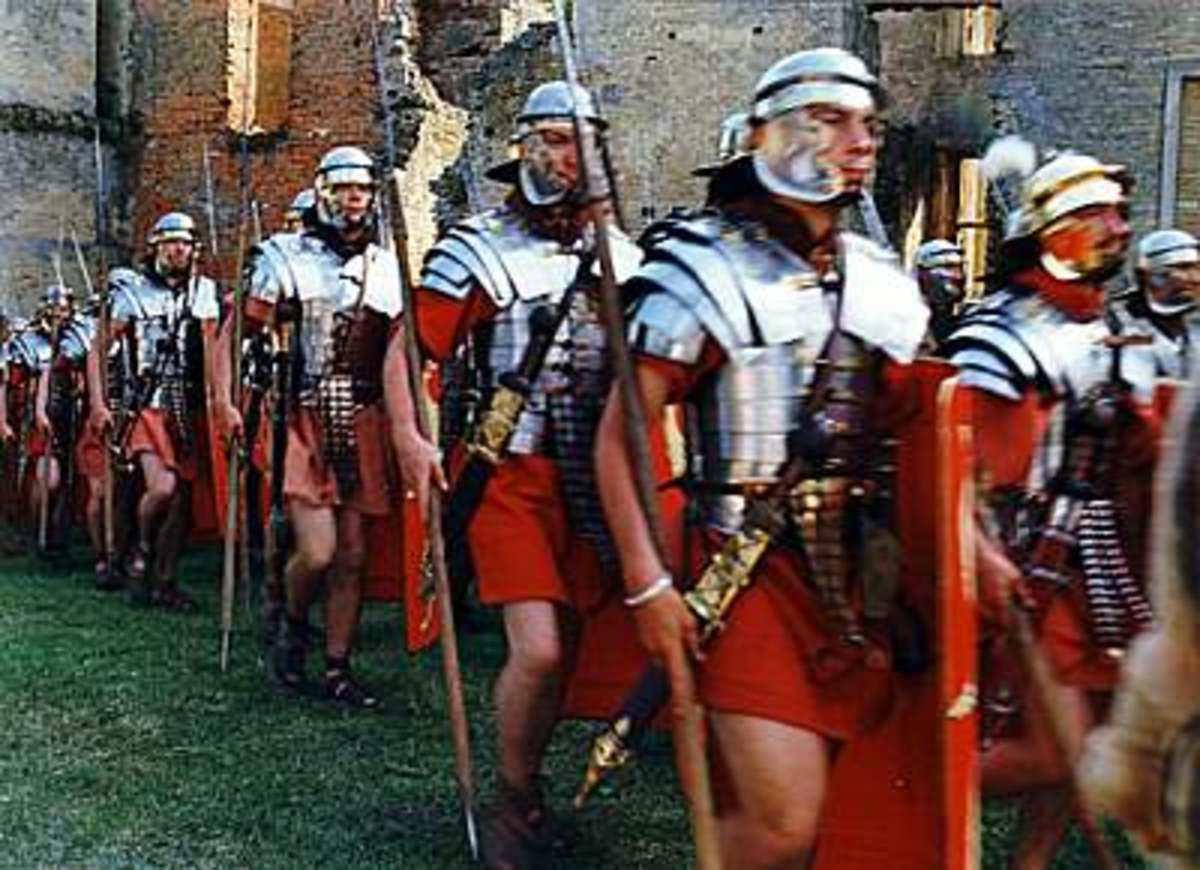

The Roman Empire Army and The Legions, Uniform & Armor Information, Images, Weaponry HubPages
In Latin, a legion was known as legio, denoting a military conscription and levy, and ultimately stemming from the word legere, to choose. The early history of Rome is not a clear as its later periods of development. However, even before the emergence of the Roman legions proper, the early army of Rome was fairly organized.

Roman Legion Wallpaper (70+ images)
A man searches for the mark of the Roman legion Legio II Augusta hidden in a secret underground chamber called Crichton Souterrain, in Southern Scotland. Written by Mark Nicol. Historian - Filmmaker - Blogger - Guided Tours - Group Speaker. Mark offers dedicated day trips that focus on experiencing these places and finding out more.
Image Roman legion tatto.jpg Riordan Wiki FANDOM powered by Wikia
Down through the centuries, millions of men served with the army of imperial Rome; half a million during the reign of Augustus alone. The history of the legions is the collective story of those individuals, not just of Rome's famous generals. Men such as Titus Flavius Virilis, still serving as a centurion at the age of 70. And Titus Calidius, a cavalry decurion who missed military life so.

Roman legion Wikipedia Military Units, Military History, Military Army, Punic Wars, Roman
Hoplite (5th Century BC) A hoplite of the Greek style. In earliest Roman history soldiers fought in much the same equipment Greek warriors used. Of the five classes defined the in the census, the first class was made up of those wealthy citizens who possessed the best armament.

Roman Legion Insignia Roman legion, Roman soldiers, Roman empire
It depends when in Rome's history we are referring to. In the days of the early republic, each legion was 4,200 men, expanding to 5,000 men in times of particular peril. After the Marian Reforms and during the Principate period of the Roman empire, each legion numbered approximately 5,200 men, sometimes rising to 6,000.

Roman Legionary Shield Legion 4 Scythica by on DeviantArt
Replacement by the soldier's mark There is some evidence suggesting that, by the time of the late Roman army, it became common practice to instead give soldiers that were found to be fit for service in the legion an indelible Soldier's Mark, possibly to discourage desertion by making any former or deserting soldiers clearly discernible.

Rome Mark Antony Rome Costume, Costumes, Rome Hbo, Rome Tv Series, Roman Armor, Mark Antony
The Roman legion was the most powerful war machine in the ancient world. While all legions played an important role, only a few gained great fame. Dec 4, 2021 • By Vedran Bileta, MA in Late Antique, Byzantine, and Early Modern History, BA in History

Roman Legionary Shield Legion 1 Germanica by on DeviantArt
This incident earned the legion its nickname Equestris (mounted). One of the legionaries jokingly said that Caesar was better than his word: he had promised to make them foot guards, but now they appeared as equestrians. [6]Legio X saved the day in the Battle against the Nervians in 57 BC. Together with the IXth, the Xth defeated the Atrebates.

Resultado de imagem para roman legion emblems Impero romano, Legione romana, Roma antica
Ancient Rome portal v t e Nero, Sestertius with countermark "X" of Legio X Gemina. Obv: Laureate bust right. Rev: Nero riding horse right, holding spear, DECVRSIO in exergue; S C across fields.

Julius Caesar Round Seal Roman legion, Roman empire, Roman history
What is a Roman Legion? Roman Legions were the basic unit of military force in the Roman Empire. A legion was responsible for keeping order in the part of the Roman world they were in..

Roman Legionary Shield Legion 1 Adiutrix Roman shield, Roman soldiers, Ancient rome history
9. Legio VI Victrix. The "Victorious Sixth Legion" was founded by the general Octavian (who later went on to become Emperor Augustus) around 41 BC. This legion is famous in the history of the imperial Roman army and was considered to be a twin of the much revered Legio VI Ferrata.

Roman Legionary Shield Legion 20 Valeria Victrtix Impero romano, Impero, Storia
The Roman legion was the backbone of the Roman army, a formidable military force that conquered much of the known world. It was a highly organized and disciplined fighting force that played a crucial role in the expansion and maintenance of the Roman Empire.

Pin by Sean on Classical World Roman armor, Roman history, Roman legion
II Traiana Fortis. This legion bore the name of its founder, the Emperor Trajan, and went on to earn the title 'fortis', meaning strong. This reflected the legion's tough military record, in particular their role in suppressing a second-century revolt in Egypt, an area known as Rome's bread basket. As the main troops in the region at.

Features the mark of the Roman Legions with Eagle and crossed gladius swords in round seal form
The Roman legion ( Latin: legiō, Latin: [ˈɫɛɡioː] ), the largest military unit of the Roman army, comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC - 27 BC) and 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire (27 BC - 476 AD). Roman legion at attack Size

I have a book titled Legions of Rome The Definitive History of Every Imperial Roman Legion by
The beginning of the Roman legions, which were not disbanded after the end of hostilities, is set to 84 BCE when Pompey the Great recruited for himself, and also for Rome, the first legion. A huge number of legionaries was set up during the civil wars in the years 49 - 30 BCE by rival leaders: Caesar, Pompey, Octavian, Antony, Brutus and Cassius.

Mapping Roman legions how “limits” tell about the centre Centres and centralities
SPQR, an abbreviation for Senatus Populusque Romanus (Classical Latin: [s̠ɛˈnäːt̪ʊs̠ pɔpʊˈɫ̪ʊs̠kʷɛ roːˈmäːnʊs̠]; English: "The Senate and People of Rome"), is an emblematic abbreviated phrase referring to the government of the ancient Roman Republic.It appears on documents made public by an inscription in stone or metal, in dedications of monuments and public works, and.