
Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
Figure 10.3.2 : Forming molecular orbitals for \(BeH_2\). Then we can put the Molecular Orbital diagram together, starting with the outside, drawing in bonding, non-bonding and anti-bonding MOs, and filling the electrons (Figure 10.3.3 ). The bond order is 2. Figure 10.3.3 : Molecular orbitals diagram for BeH 2.

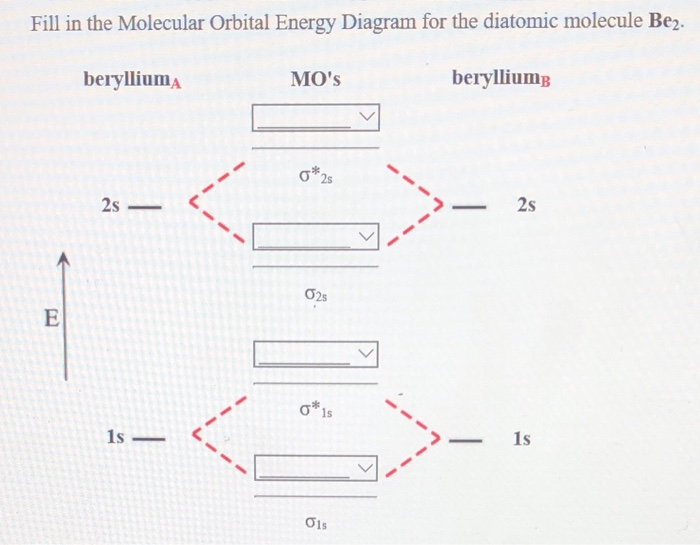
Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Be2. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Be
1. Write down the electronic configuration of Be2 atoms Be 2 comprises two identical beryllium (Be) atoms. The electronic configuration of each Be-atom is 1s2 2s2. Usually, only the valence electrons are displayed in the MO diagram of a molecule, therefore, it is important to note that each Be-atom contains 2 valence electrons only.

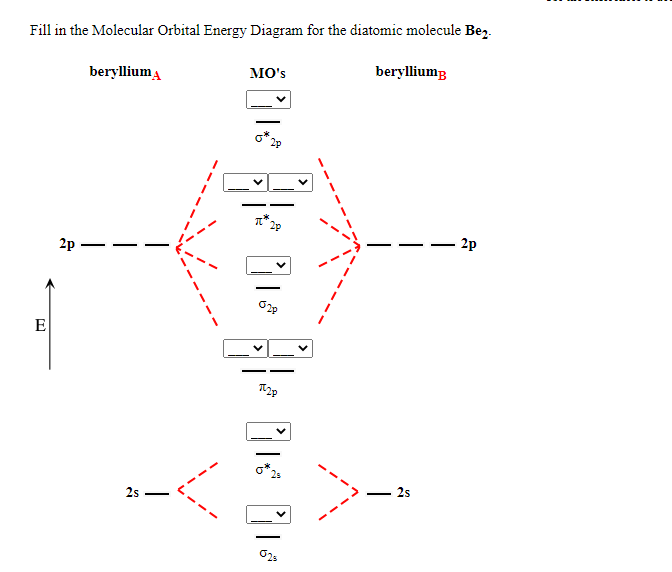
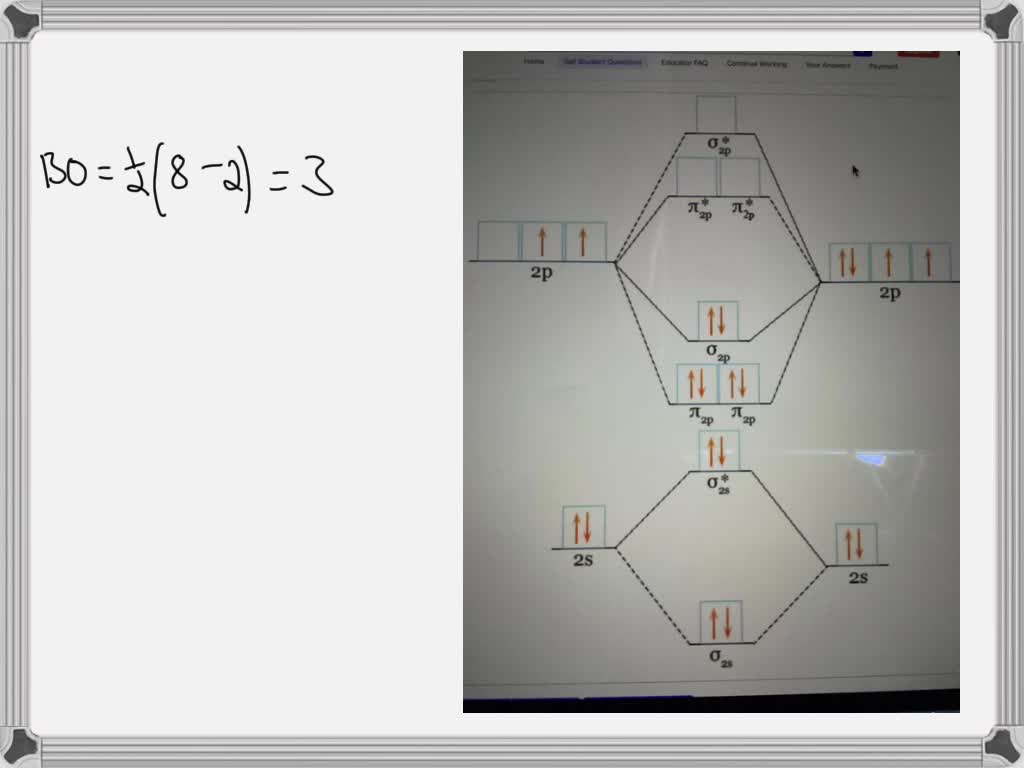
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for (i) Be2 (ii) O2 and predict bond order, stability and
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of.
Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram ADE
Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Be2. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Be Ho Be Answer Bank IL | Identify the bond order. O 0 O os O 1s This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer
Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Beryllium Dimer (Be2)Fill from the bottom up, with 4 electrons total.Bonding Order is 0, meaning it does not bond, and it is di.
Solved Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the
Principia 263 subscribers Subscribe 48 Share 6.7K views 2 years ago Molecular Orbital Diagrams This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the Be2 molecule. The.

Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
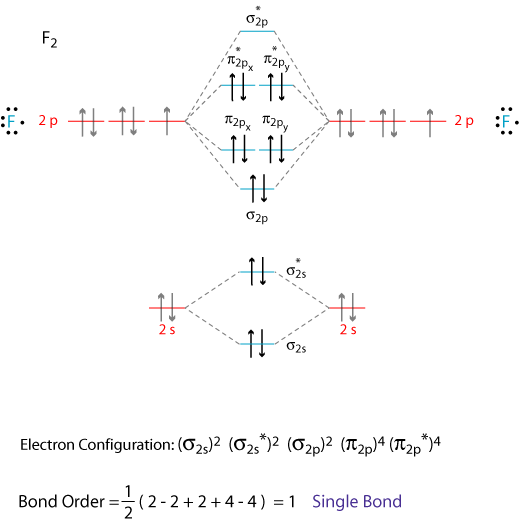
Textbook Question The C2 molecule has a MO diagram similar to N2 (Figure 8.22a). What is the bond order of C2 and is it paramagnetic or diamagnetic? (LO 8.12) (a) Bond order = 2, diamagnetic (b) Bond order = 2, paramagnetic (c) Bond order = 0, paramagnetic (d) Bond order = 3>2, diamagnetic
Molecular Orbitals and Hybridizations Organic Chemistry Socratic
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the Be2+ ion. The bond order of Be2+ is also calculated and the meaning of this numbe.

Molecular Orbital Theory Build Be2 YouTube
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic \(\ce{Be2+}\), showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule.

Shorter is higher the strange case of diberyllium. Henry Rzepa's Blog Henry Rzepa's Blog
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+,Be2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2
For the ion Be2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion————.

Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
Answer Advertisement Zigya App Draw the molecular orbital diagram for: (i) Be2 (ii) B2 and predict bond order and magnetic properties. (i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be (Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2

Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram ADE
Figure 9.8.4: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for a Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecule AB, Where χ B > χ A. The bonding molecular orbitals are closer in energy to the atomic orbitals of the more electronegative B atom. Consequently, the electrons in the bonding orbitals are not shared equally between the two atoms.

Molecular Orbital Diagram For Be2
A molecule must have as many molecular orbitals as there are atomic orbitals. Figure 9.7.1 9.7. 1: Molecular Orbitals for the H 2 Molecule. (a) This diagram shows the formation of a bonding σ 1s molecular orbital for H 2 as the sum of the wave functions (Ψ) of two H 1 s atomic orbitals.

2.7 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry for Chemical Engineers
The molecular orbital diagram of Be2 can be visualized by considering the atomic orbitals of the two beryllium atoms: 2s and 2p. When these orbitals combine, they form two molecular orbitals: a bonding molecular orbital (σ) and an antibonding molecular orbital (σ*). The bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy and can hold a maximum of 2.
Be2 Molecular Orbital Diagram
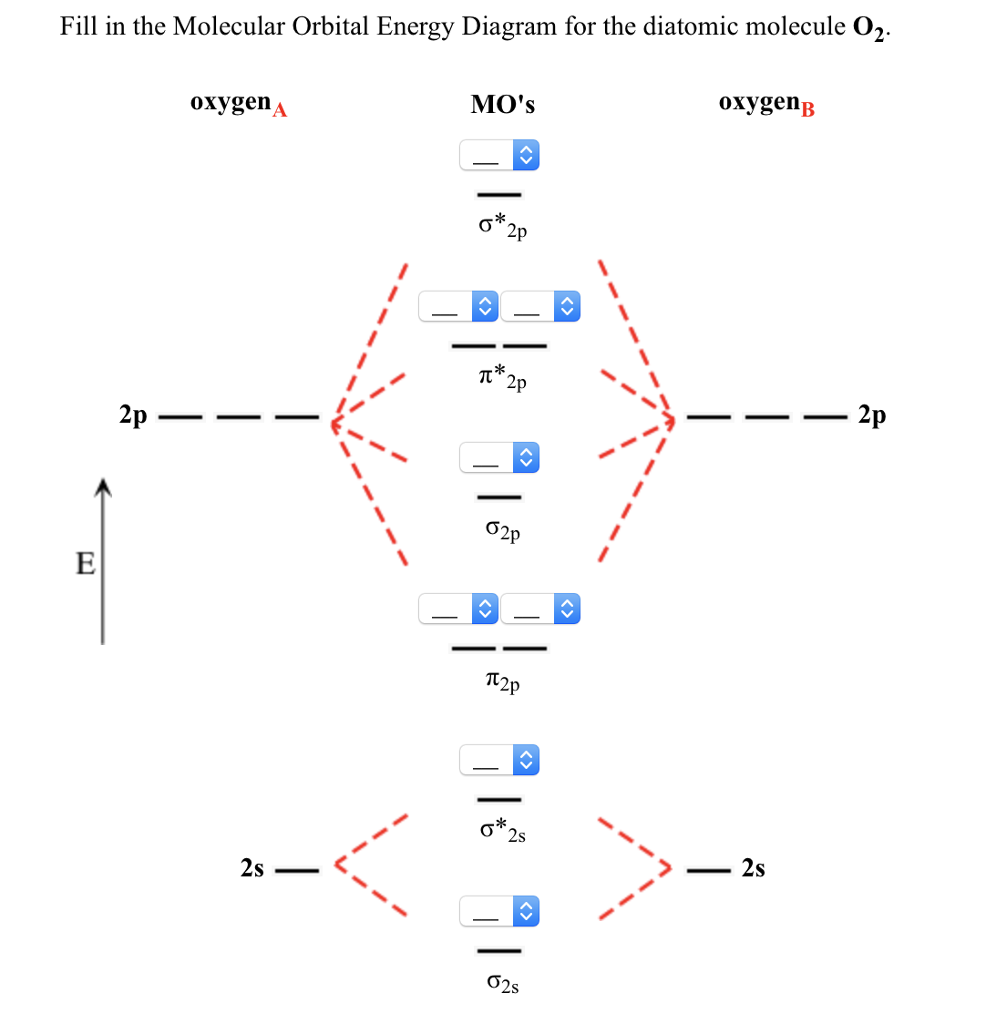
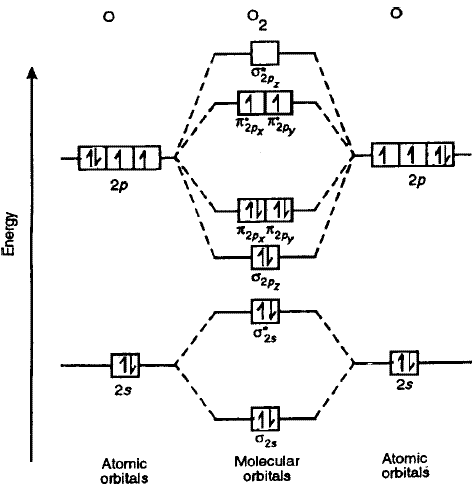
paramagnetism , and it arises in molecules that have unpaired electrons. And yet, the Lewis structure of O 2 indicates that all electrons are paired. How do we account for this discrepancy? Figure 7.7.1. Oxygen molecules orient randomly most of the time, as shown in the top magnified view.