
The Norton Scale PDF Sensitivity And Specificity Validity
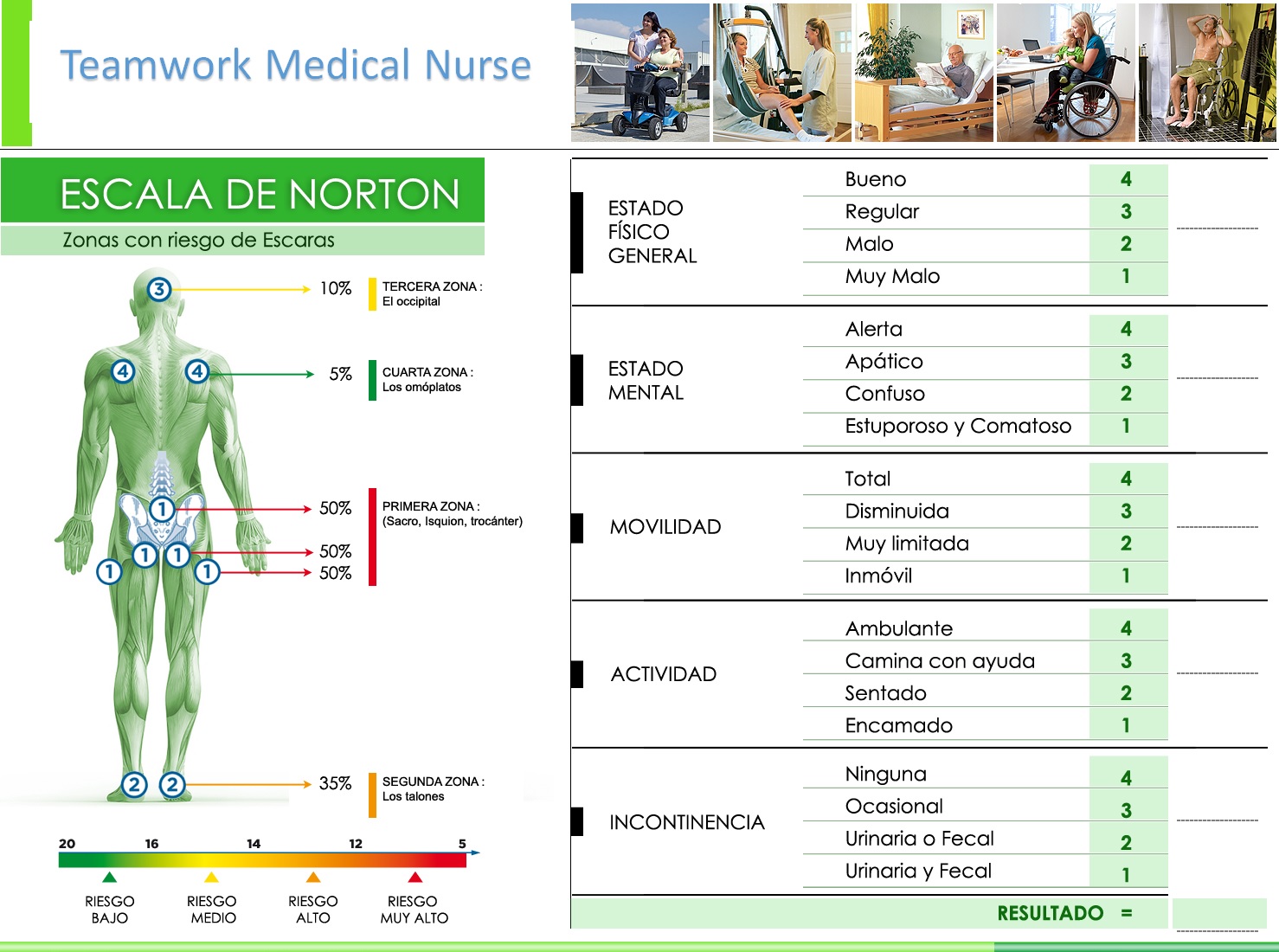
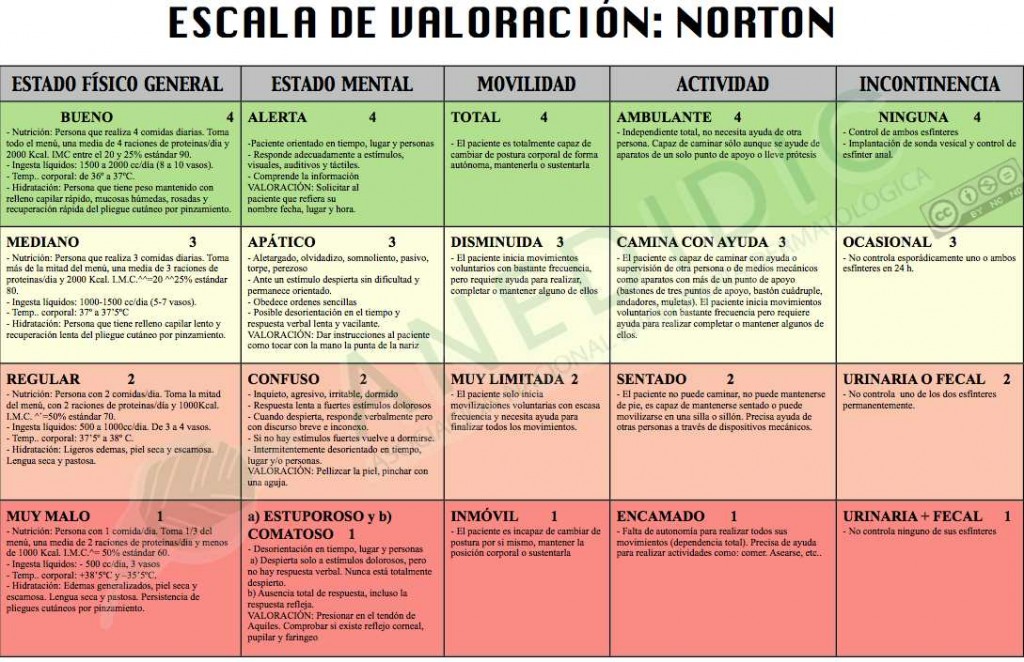
Introduction. The Norton scale scoring system [1] was created in 1962 to assess the risk of pressure sores during hospitalization and is still being used nowadays by nurses. It consists of 5 variables: physical and mental condition, activity, mobility, and incontinence. Each variable is graded from 1 to 4 with maximum score of 20 (Online Table 1).Since it was first introduced, almost sixty.

THE AGEING PRESSURE ULCERS
Pathophysiology Symptoms and Signs Complications Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis Prevention Key Points More Information Pressure injuries are areas of necrosis and often ulceration (also called pressure ulcers) where soft tissues are compressed between bony prominences and external hard surfaces.

Norton Scale For Pressure Ulcer Risk Assessment This Scale Was Created
The Norton Scoring system, shown below, and created in England in 1962, has been the first pressure sore risk evaluation scale to be created, back in 1962, and for this it is now criticized in the wake of the results of modern research. Its ease of use, however, makes it still widely used today.
Escala de Norton Página web de pseudomonas
This Norton score for pressure ulcer risk calculator is used in the evaluation of sore risk based on patient factors such as mobility or physical condition. There is more information about this scale below the form as well as an interpretation of its possible results. 1 Physical condition

(PDF) Assessment of risk for pressure ulcers using the Norton scale in
The Norton Scale is made up of five subscales (physical condition, mental condition, activity, mobility, incontinence) scored from 1-4 (1 for low level of functioning and 4 for highest level of functioning). The subscales are added together for a total score that ranges from 5 to 20. A lower Norton Scale score indicates higher levels of risk.

Norton Reveals The Shocking Scale Of Cyber Crime In Asia Gambaran
This Norton score calculator calculates the bedside risk that a person has of obtaining pressure ulcers. Physical condition Good +4 Fair +3 Poor +2 Very Bad +1 Mental condition Alert +4 Apathetic +3 Confused +2 Stupor +1 Activity Ambulant +4 Walks with help +3 Chairbound +2 Bedbound +1 Mobility Full +4 Slightly limited +3 Very limited +2 Immobile

Pearson's correlation between admission Norton scale scores and the
The Norton scale consists of five risk factors that have been classified into scores that provide the final classification of risk for PU, as follows: high risk: less than or equal to 12 and low risk: greater than 12 points [13, 14]. The Waterlow scale is divided into 11 risk factors that allow for assessment of the risk of PU.

Pressure Ulcers in Older Adults Objectives l l
Date: March 9, 2023 The Norton Pressure Ulcer Risk-Assessment Scale is a tool designed to help clinicians evaluate patients' risk of developing pressure injuries. Nurse Doreen Norton developed the scale in 1962 and it has been widely used since its creation.
Nursing cares in the elderly patients. PRESSURE ULCERS
The aim of this project was to modify the Norton Scale for Pressure Sore Risk to improve its predictive power when used in the critical care setting. PARTICIPANTS AND SETTING: The setting for this quality improvement project was a 1157-bed academic medical center in the Southeast United States. Data were collected from 114 clinicians; 111 were.

Table 3 from Interrater Reliability of Items of the Braden Scale, the
The Norton Scale (and modified versions) and the effect of the scale on care plans was used in the studies of clinical effectiveness. For inclusion, studies were required to offer data on the predictive values of the scales (sensitivity and specificity) or raw data for calculation of these.

Nortonscale.pdf Urinary Incontinence Medical Specialties
The Norton Scale was developed in the 1960s and is widely used to assess the risk for pressure ulcer in adult patients. The five subscale scores of the Norton Scale are added together for a total score that ranges from 5-20. A lower Norton score indicates higher levels of risk for pressure ulcer development.
Pressure Ulcers Prevention and Treatment Jennifer A Gardner Wound Care
R600. BRIGGS, Des Moines, IA 50306 (800) 247-2343. PRINTED IN U.S.A. SOURCE:Doreen Norton, Rhoda McLaren and AN Exton-Smith, An Investigation of Geriatric Nursing Problems in Hospital, National Corporation for the Care of Old People (now Centre for Policy on Ageing), London, 1962. NORTON PLUS PRESSURE ULCER SCALE.

PPT PRESSURE ULCERS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2776919
Different risk assessment tools that have been developed; the most widely used is the Braden and Norton Scales discussed above. Personnel. The wound management team is responsible for taking care of any patient with pressure sores. This team usually includes the primary attending, dermatologist and/or plastic surgeon, nurse, nurse assistant.

Characteristics of patients with low and high admission Norton scale
The Norton Scale was the second most efficient predictor (60.2% correct), with 46.8% sensitivity, 61.8% specificity and an odds ratio of 2.16 of correctly predicting a PU based on 5 studies on 2,008 patients. Low specificity decreased predictive efficacy of the Waterlow Scale (34.4% correct) to below the 58.0% reported for clinical judgment.

(PDF) Evaluation of a Modified Version of the Norton Scale for Use as a
The Norton Scale Is One Bedsore Assessment Tool. According to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, the Norton Scale was developed in the 1960s and is used to assess an adult's risk of developing a pressure ulcer. The person conducting the assessment must assess five categories and assign a number of 1-4 for each category.
Norton Scale 4 Pressure Ulcer Android Apps on Google Play
The Norton Scale for Predicting Pressure Ulcer Risk*. * Calculated as the sum of the scores in all 5 areas. A score < 14 indicates a high risk of pressure ulcer development. Adapted from Norton, D: Calculating the risk: Reflections on the Norton scale. Decubitus 2 (3):24-31, 1989.