
Resultado de imagen de posicion antitrendelemburg Gym, Gym equipment, Row machine
The Ultimate Guide to the Trendelenburg Position. Positioning is imperative to patient safety during a surgical procedure. Proper patient positioning depends on the type and length of procedure, anesthesia access to the patient, devices required and other factors.

Operating Room Patient Positioning The Operating Room Global
Currently, the Trendelenburg position is often used in lower abdominal surgeries, including colorectal, gynecological, and genitourinary procedures. In this position, gravity pulls the intra-abdominal organs away from the pelvis, allowing for better surgical access to the pelvic organs. In critical care settings, the Trendelenburg position is.
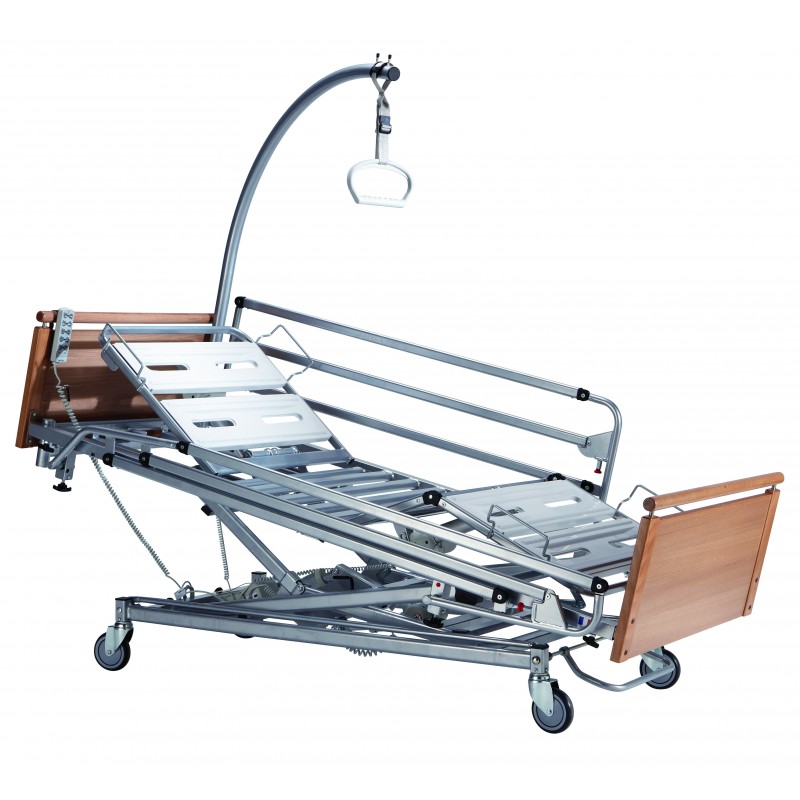

Antitrendelenburg bed
The Anti-Trendelenburg position, also known as the Reverse-Trendelenburg position, involves placing the patient in the same position at an incline of between 15 and 30 degrees. In this case, though, the head is than the legs. German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg invented the position; he used this method initially to improve the exposure of.
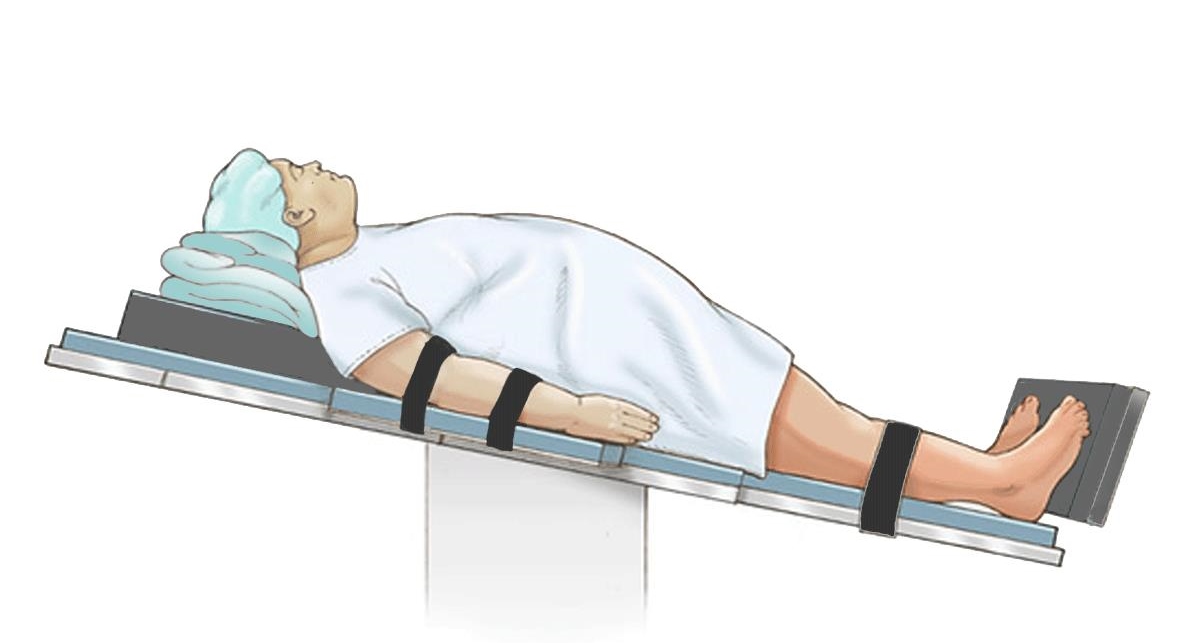
24 TES Posiciones, direcciones, planos y cavidades anatómicas.
The Anti-Trendelenburg position increases intracranial pressure, which can lead to brain problems such as hemorrhage, edema, and ischemia. Respiratory Complications. The Anti-Trendelenburg position can cause respiratory complications, especially in patients with respiratory distress. The position can cause decreased lung volume, hypoxemia, and.

Antitrendelenburg bed
What is the Trendelenburg Position on hospital beds? - Innova Care Concepts

Trendelenburg/AntiTrendelenburg position for C213 [LIGHT] Medical furniture, massage tables
Hypovolemia is a common clinical problem. The Trendelenburg position and passive leg raising (PLR) are routinely used in the initial treatment while awaiting fluid resuscitation. In this meta-analysis, we evaluated the hemodynamic effects of PLR and Trendelenburg positioning to determine which posit.

position antiTrendelenburg GDT
Purpose of review: Laparoscopy is routinely performed for the treatment and management of gynaecologic disorders. During gynaecologic laparoscopy, the patient is placed in the Trendelenburg position to optimize visualization and access to the pelvis.

TRENDELENBURG POSITION REVERSE TRENDELENBURG POSITION [DEFINITION AND USES] YouTube
Low fluid levels could result in acute renal failure, so it's important to find the right balance between maximum exposure of the surgical field and sufficient fluid use. 2. Standardize protocols. It's important to root out any inconsistencies in patient positioning practices because even minor variations can lead to major safety problems.

Trendelenburg Positioner Trendelenburg Stabilizer
The Trendelenburg position involves placing the patient head down and elevating the feet. It is named after German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg (1844-1924), who created the position to improve surgical exposure of the pelvic organs during surgery. In World War I, Walter Cannon, the famous American physiologist, popularized the use of.
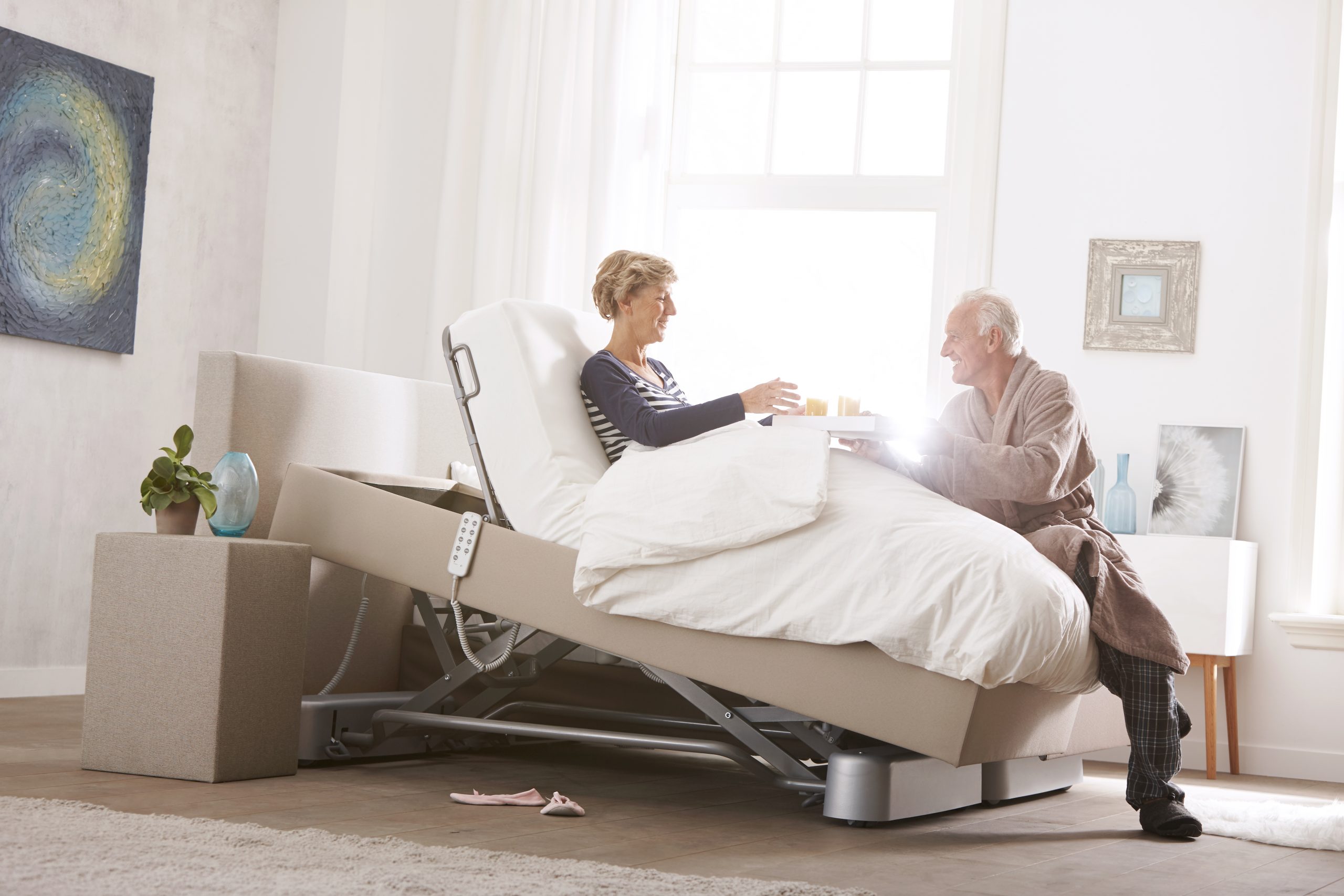

Anti Trendelenburg functie voordelen
Background. Postoperative cognitive decline (POCD) is defined as a new cognitive impairment arising after a surgical intervention. Aspects of cognitive function can be assessed using various validated cognitive function tests including the N-back task, the Stroop task, and the lexical decision-making task (LDT).
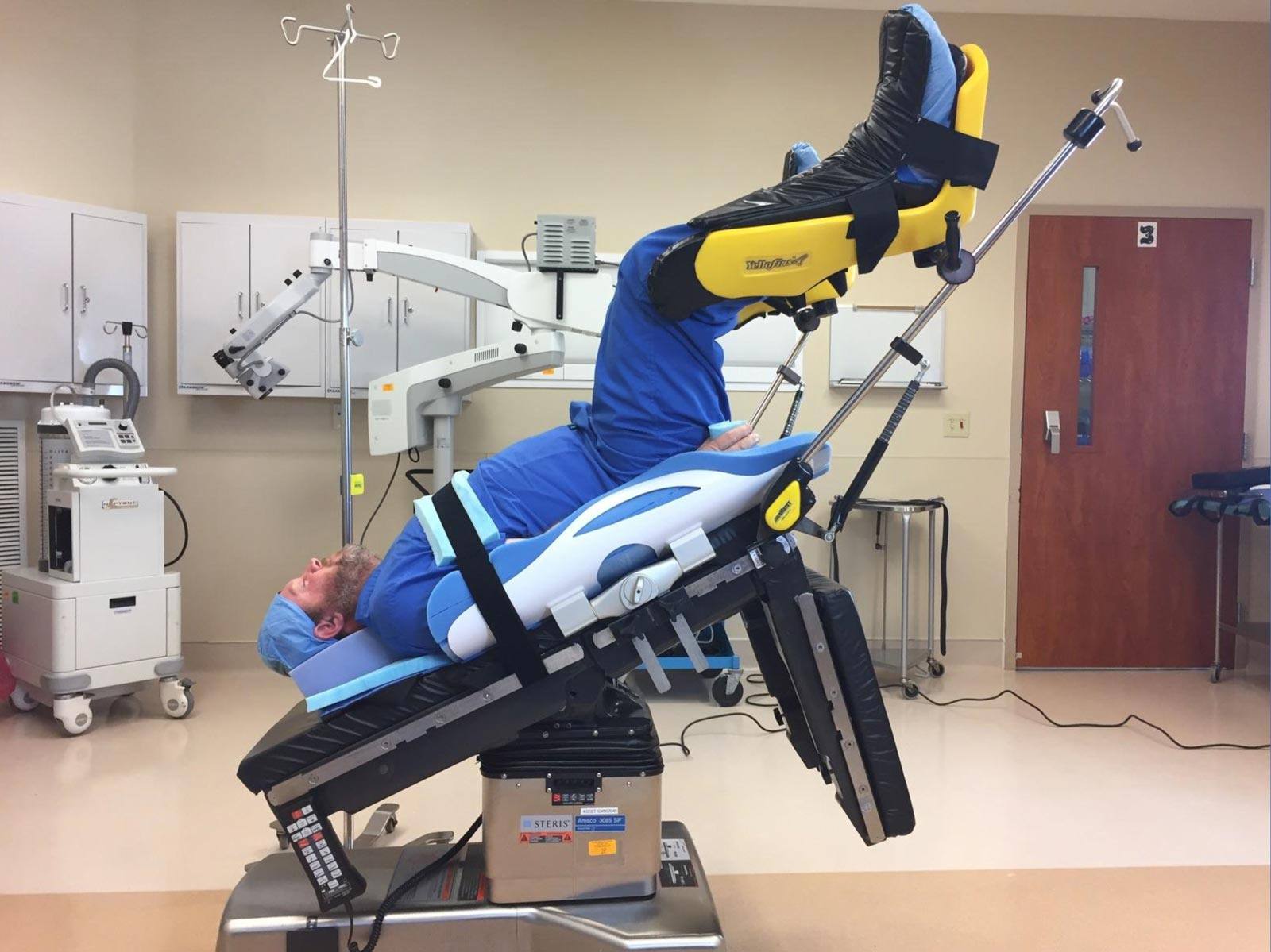
Hadron FLPS® Trendelenburg Positioning Pad KLM Medical Equipment
What is the Anti-Trendelenburg position? The Anti-Trendelenburg - also known as Reverse-Trendelenburg - is where the head is elevated higher than the feet by 15-30 degrees. Again, this position has been used in surgical and medical procedures to improve access to certain parts of the body, like the prostate and upper abdominal region.
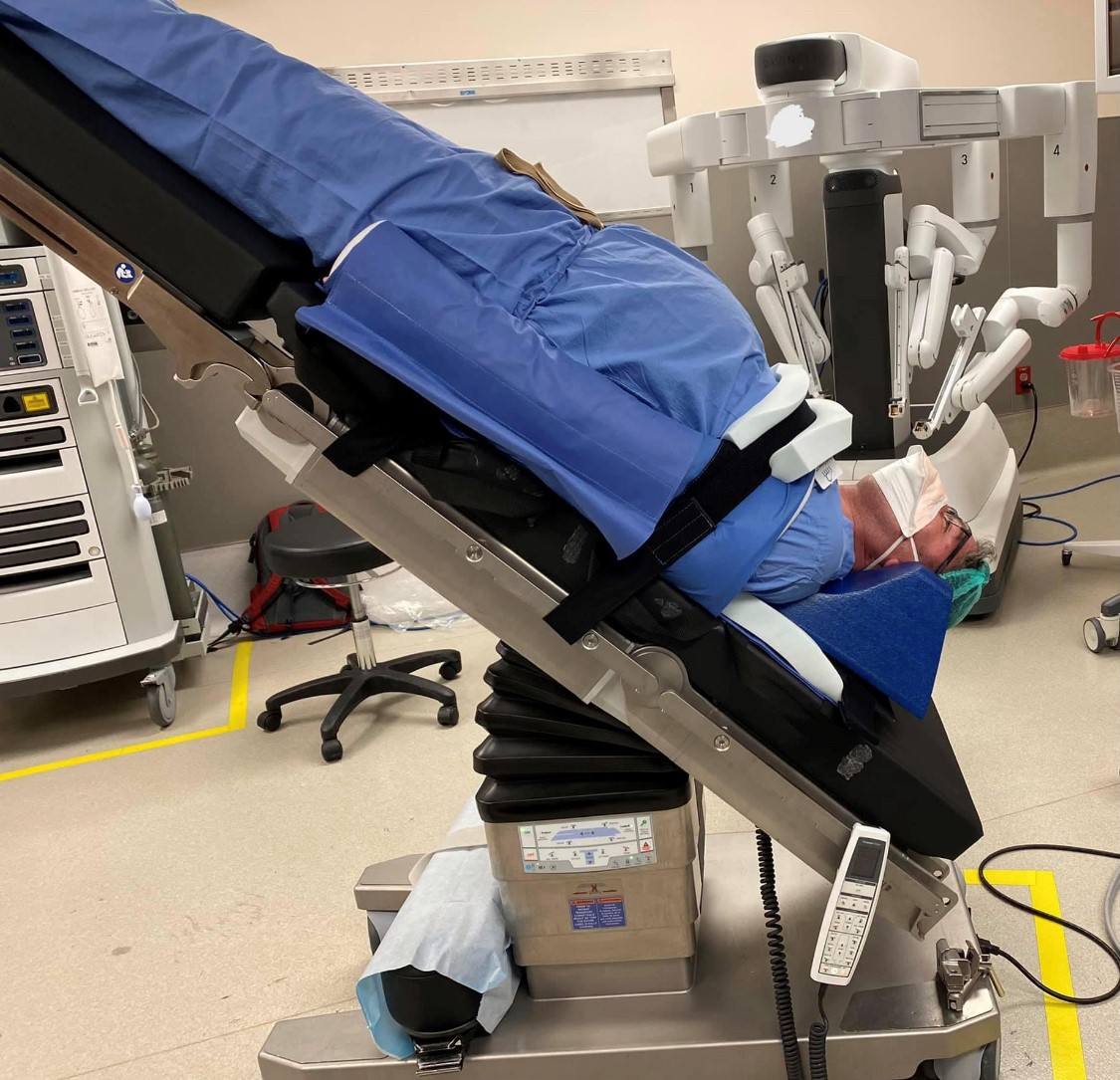
Trendelenburg Positioning Pad System, Robotic Surgery Face Protection
The Trendelenburg position is also used when placing a central venous catheter in the internal jugular or subclavian vein. The Trendelenburg position uses gravity to assist in the filling and distension of the upper central veins, as well as the external jugular vein. It plays no role in the placement of a femoral central venous catheter.

¿Qué es posición Trendelenburg y AntiTrendelenburg?
Nombrada en honor al cirujano alemán Friedrich Trendelenburg, la posición de Trendelenburg implica que el paciente está acostado sobre su espalda en una cama o camilla que se inclina con los pies más altos que la cabeza, generalmente en un ángulo de alrededor de 15 a 30 grados. Esta posición particular tiene varios usos médicos.

Storm Anesthesia Trendelenburg
Así como la posición Trendelenburg consiste en la elevación de los pies sobre la cabeza, la posición Anti-Trendelenburg es exactamente lo contrario. Es decir, igualmente los pacientes en esta postura se encuentran boca arriba, pero en esta ocasión la cabeza queda en un ángulo más elevado que las extremidades.
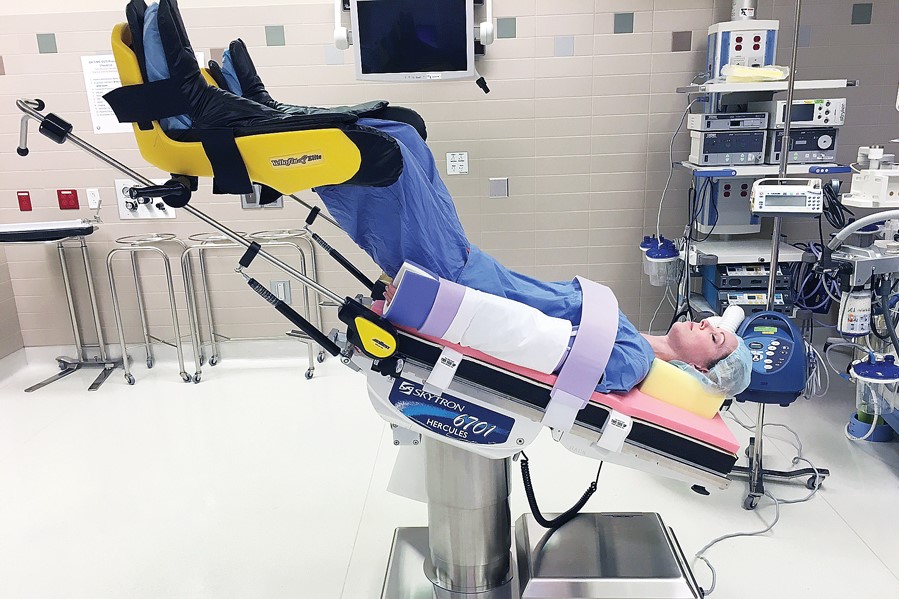
Trendelenburg (antishock) positie wat het is en wanneer het wordt aanbevolen
How and when the reverse Trendelenburg position is practised. It is practised in articulated hospital beds and involves tilting the bed at 25-30° so that the head and chest are on a higher plane than the feet (supine patient). It has benefits on the skull for the counter extension of spinal injuries; it aids the surgical drainage of pleural.

24 TES ¿En qué posición debemos de trasladar al paciente?
Posición de Trendelenburg. En la ciencia de la medicina, la posición de Trendelenburg es aquella en que se coloca al paciente en decúbito supino y con la cabeza más baja que los pies, de tal forma que se favorece por efecto de la gravedad el retorno de la sangre venosa hacia el corazón a través de la vena cava inferior. 1 2 .